What is the Op Amp?
Have you ever wondered what an op amp is and how it works? Operational amplifiers, often abbreviated as op amps, are one of the most fundamental components in electronic circuits. They are used in a wide range of applications, from audio amplifiers to medical equipment. In this detailed guide, we will explore the ins and outs of op amps, their characteristics, and their applications.
Understanding the Basics

At its core, an op amp is an electronic device that amplifies voltage. It consists of a differential amplifier, which compares two input voltages, and an output stage that amplifies the difference between these voltages. The output of an op amp can be either positive or negative, depending on the configuration of the circuit.
Op amps are typically represented by a symbol that looks like a triangle with two inputs and one output. The inputs are labeled as “inverting” and “non-inverting,” and the output is labeled as “output.” The inverting input is denoted by a negative sign, while the non-inverting input is denoted by a positive sign.
Characteristics of Op Amps

There are several key characteristics that define an op amp:
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| High Input Impedance | The input impedance of an op amp is typically very high, which means it draws very little current from the input signal source. |
| Low Output Impedance | The output impedance of an op amp is typically very low, which means it can drive loads with minimal signal loss. |
| High Gain | The gain of an op amp is very high, typically in the range of 100,000 to 1,000,000. This allows for precise control of the output signal. |
| Wide Bandwidth | The bandwidth of an op amp is the range of frequencies over which it can amplify signals effectively. A wide bandwidth is important for applications that require high-frequency signal processing. |
| Low Offset Voltage | The offset voltage is the voltage difference between the two inputs when the output is at zero. A low offset voltage is desirable for precision applications. |
Types of Op Amps
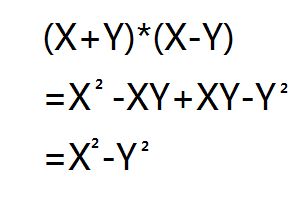
There are several types of op amps, each with its own set of characteristics and applications:
- Single-supply op amps: These op amps are designed to operate with a single supply voltage, making them suitable for battery-powered applications.
- Dual-supply op amps: These op amps require a positive and negative supply voltage, which allows for a wider output voltage range.
- Low-power op amps: These op amps are designed to consume very little power, making them suitable for portable devices.
- High-speed op amps: These op amps are designed for high-frequency applications, such as communication systems.
Applications of Op Amps
Op amps are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Audio amplifiers: Op amps are used to amplify audio signals, such as those from microphones or musical instruments.
- Signal conditioning: Op amps are used to filter, amplify, and shape signals for various applications.
- Instrumentation amplifiers: These amplifiers use op amps to amplify low-level signals from sensors and transducers.
- Filter design: Op amps are used to design various types of filters, such as low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters.
- Control systems: Op amps are used in control systems to amplify and process signals, allowing for precise control of devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, op amps are essential components in electronic circuits, providing high gain, low noise, and precise control of signals. With their wide range of applications, op amps are a cornerstone of modern electronics. Whether you are designing an audio amplifier or a medical device, understanding how op amps work
