Rail-to-Rail Op Amp List: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), the term “rail-to-rail” refers to the ability of the amplifier to output signals that swing from the negative supply voltage to the positive supply voltage, effectively utilizing the full range of the power supply. This feature is highly desirable in many applications, especially those requiring high output voltage swing. In this article, we will delve into the world of rail-to-rail op-amps, exploring their specifications, applications, and some of the most popular models available in the market.
Understanding Rail-to-Rail Op Amps
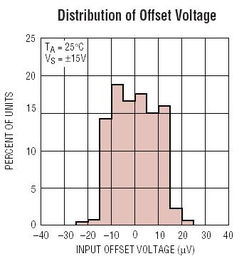
Rail-to-rail op-amps are designed to provide a wider output voltage range compared to traditional op-amps. This is achieved by using a differential input stage that can operate close to both the positive and negative supply voltages. As a result, rail-to-rail op-amps can deliver output voltages that are closer to the supply voltages, which is particularly useful in applications where the output signal needs to reach the power supply rails.
One of the key advantages of rail-to-rail op-amps is their improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). This is because the input stage can operate closer to the power supply rails, reducing the impact of noise and fluctuations in the power supply voltage on the output signal.
Applications of Rail-to-Rail Op Amps

Rail-to-rail op-amps find applications in a wide range of electronic systems, including audio amplifiers, data acquisition systems, and battery-powered devices. Some of the common applications include:
-
Audio Amplifiers: Rail-to-rail op-amps are commonly used in audio amplifiers to provide a wider output voltage range and improved sound quality.
-
Data Acquisition Systems: These systems often require high-resolution and low-noise amplification, making rail-to-rail op-amps an ideal choice.
-
Battery-Powered Devices: Rail-to-rail op-amps are well-suited for battery-powered devices, as they can provide a wider output voltage range and improved efficiency.
Key Specifications of Rail-to-Rail Op Amps
When selecting a rail-to-rail op-amp, it is important to consider several key specifications to ensure that it meets the requirements of your application. Some of the important specifications include:
-
Input Offset Voltage: This is the voltage difference between the two input terminals when the output is at zero volts. A lower input offset voltage is desirable for applications requiring high precision.
-
Input Bias Current: This is the current flowing into the input terminals of the op-amp. A lower input bias current is desirable for applications with high impedance inputs.
-
Output Voltage Swing: This is the maximum voltage that the op-amp can output, measured from the negative supply voltage to the positive supply voltage. A wider output voltage swing is desirable for applications requiring signals close to the power supply rails.
-
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR): This is a measure of the ability of the op-amp to reject noise and fluctuations in the power supply voltage. A higher PSRR is desirable for applications requiring low noise and high stability.
Popular Rail-to-Rail Op Amp Models
There are numerous rail-to-rail op-amp models available in the market, each with its own set of features and specifications. Here are some of the most popular models:
| Model | Supply Voltage (V) | Input Offset Voltage (mV) | Input Bias Current (nA) | Output Voltage Swing (V) | PSRR (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMV358 | 2.7 to 5.5 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.8 to 3.5 | 86 |
| TLV272 | 2.7 to 5.5 | 0.5 |
