Op Amp Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide
Operational amplifiers, often referred to as op amps, are fundamental components in electronic circuits. They are versatile and widely used in various applications, from signal amplification to filtering and oscillation. Understanding the op amp diagram is crucial for anyone working with electronic circuits. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the op amp diagram, exploring its components, working principles, and practical applications.
Components of an Op Amp Diagram
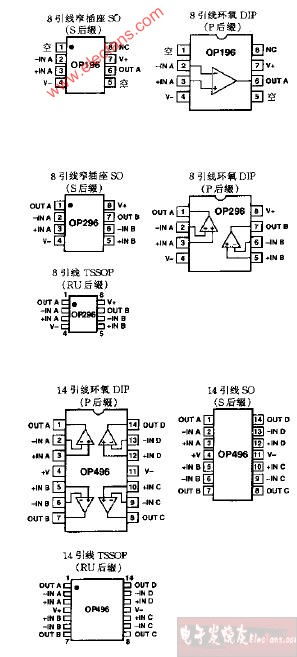
The op amp diagram consists of several key components that work together to perform various functions. These components include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Terminal | Used to apply the input signal to the op amp. |
| Output Terminal | Delivers the amplified or processed signal from the op amp. |
| Power Supply Terminals | Provide the necessary voltage to power the op amp. |
| Feedback Network | Connects the output terminal to the input terminal, controlling the gain and stability of the op amp. |
These components work together to ensure that the op amp operates as intended. The input terminal receives the signal, the power supply terminals provide the necessary voltage, and the feedback network controls the gain and stability of the amplified signal.
Working Principles of an Op Amp Diagram
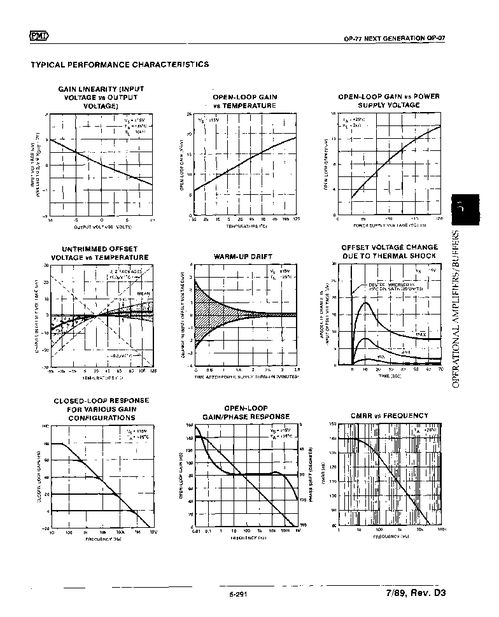
The working principles of an op amp diagram are based on the concept of negative feedback. Negative feedback is a technique used to stabilize the output of the op amp and control its gain. Here’s how it works:
- The input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp.
- The op amp amplifies the input signal by a factor determined by the feedback network.
- The amplified signal is then fed back to the inverting input terminal through the feedback network.
- The op amp compares the feedback signal with the input signal and adjusts its output accordingly to maintain a stable output.
This process ensures that the op amp operates with high accuracy and stability. The gain of the op amp can be controlled by adjusting the components in the feedback network.
Practical Applications of Op Amp Diagrams
Op amp diagrams are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some common applications:
-
Signal Amplification: Op amps are used to amplify weak signals, making them suitable for applications such as audio amplifiers, medical equipment, and wireless communication systems.
-
Filtering: Op amps can be used to filter out unwanted noise from a signal, making them ideal for applications such as audio processing, data acquisition, and control systems.
-
Oscillation: Op amps can generate stable oscillating signals, which are essential for applications such as timing circuits, frequency generators, and signal generators.
-
Comparator: Op amps can be used as comparators to compare two signals and provide a digital output based on the comparison result, making them suitable for applications such as analog-to-digital conversion and sensor interfacing.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of op amp diagrams. The versatility of op amps makes them a crucial component in electronic circuits across various industries.
Conclusion
Understanding the op amp diagram is essential for anyone working with electronic circuits. By familiarizing yourself with the components, working principles, and practical applications of op amp diagrams, you can design and implement more efficient and effective electronic circuits. Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, or professional, mastering the op amp diagram will undoubtedly enhance your skills and knowledge in the field of electronics.
