Clinical Ops: A Comprehensive Guide
Clinical operations, often abbreviated as “clinical ops,” play a pivotal role in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries. These operations encompass a wide array of activities, from planning and executing clinical trials to managing data and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the various aspects of clinical ops, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this critical field.
Understanding Clinical Operations
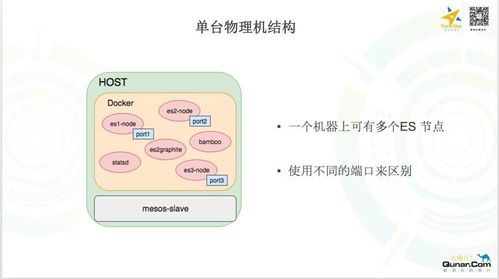
Clinical operations involve the coordination and management of all activities related to clinical trials. This includes everything from the initial planning stages to the final analysis and reporting of trial results. The goal of clinical ops is to ensure that trials are conducted efficiently, ethically, and in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key Components of Clinical Operations

Here are some of the key components that make up clinical operations:
-
Study Design and Planning: This involves determining the objectives, methodology, and scope of the trial. It also includes identifying the appropriate endpoints and selecting the right participants.
-
Site Selection and Management: Clinical ops teams are responsible for identifying and selecting clinical trial sites, as well as managing these sites throughout the trial.
-
Recruitment and Enrollment: This involves identifying potential participants, obtaining their consent, and enrolling them in the trial.
-
Data Management: Clinical ops teams are responsible for collecting, managing, and analyzing data from the trial. This includes ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that all aspects of the trial comply with regulatory standards is a critical aspect of clinical ops.
-
Monitoring and Oversight: Clinical ops teams monitor the progress of the trial and ensure that it is being conducted as planned.
-
Reporting and Publication: Once the trial is complete, clinical ops teams are responsible for preparing and submitting reports to regulatory authorities and publishing the results in scientific journals.
The Role of Technology in Clinical Operations
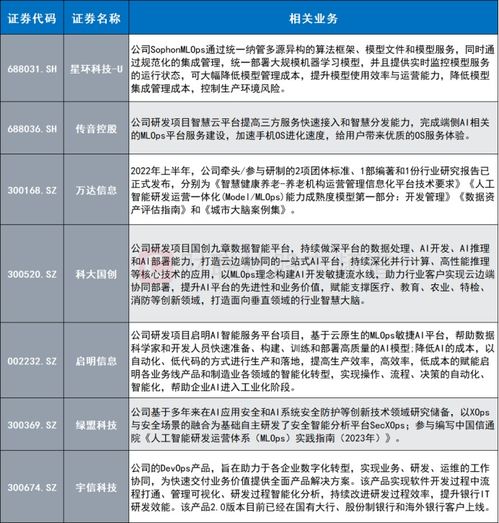
Technology has become an integral part of clinical operations, helping to streamline processes and improve efficiency. Here are some of the key technologies used in clinical ops:
-
Electronic Data Capture (EDC): EDC systems are used to collect, manage, and analyze data from clinical trials. These systems can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with data management.
-
Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF): eTMFs are used to store and manage all documents related to a clinical trial. They provide a centralized repository for all trial-related information, making it easier to access and share data.
-
Electronic Patient Reporting (ePRO): ePRO systems allow patients to report their symptoms and side effects directly to the study team, improving data quality and reducing the need for manual data entry.
-
Cloud Computing: Cloud-based solutions are used to store and manage large volumes of data, providing scalability and flexibility for clinical ops teams.
The Challenges of Clinical Operations
While clinical operations are essential for the success of clinical trials, they also come with their own set of challenges. Some of the most common challenges include:
-
Recruitment and Enrollment: Finding and enrolling the right participants can be difficult, especially for trials involving rare diseases or complex interventions.
-
Data Management: Ensuring data integrity and accuracy is a significant challenge, especially when dealing with large volumes of data.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up with changing regulations and ensuring compliance can be a complex and time-consuming task.
-
Resource Allocation: Balancing the needs of different stakeholders, such as sponsors, investigators, and patients, can be challenging.
Best Practices for Successful Clinical Operations
Here are some best practices that can help ensure the success of clinical operations:
-
Effective Communication: Clear and open communication among all stakeholders is essential for successful clinical operations.
-
Strategic Planning: Developing a well-thought-out plan for each trial can help identify potential challenges and mitigate risks.
-
Skilled Team: Assembling a team with the right skills and experience is crucial for successful clinical operations.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and improving processes can help
