Precision Current Source Op-Amp Circuit: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the intricacies of a precision current source operational amplifier (op-amp) circuit is crucial for anyone delving into the world of analog electronics. This guide will walk you through the basics, the components, the operation, and the applications of such a circuit, ensuring you have a thorough grasp of its functionality.
Understanding the Basics
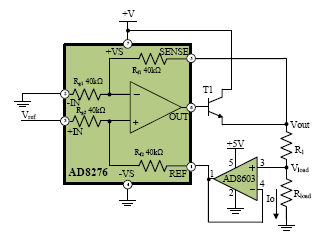
A precision current source op-amp circuit is designed to provide a stable and accurate current output. Unlike a voltage source, which maintains a constant voltage across its terminals, a current source maintains a constant current through its terminals, regardless of the load resistance. This makes it an essential component in many applications, including data acquisition systems, precision measurement circuits, and power supplies.
Components of the Circuit
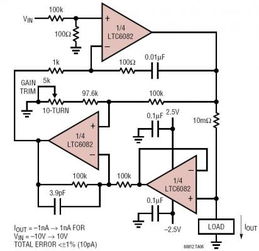
The core of a precision current source op-amp circuit is the operational amplifier. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) | A high-gain voltage amplifier with differential inputs and a single output. It is the heart of the circuit, providing the necessary gain and stability. |
| Resistor | Used to set the desired current output. The value of the resistor determines the current through the circuit. |
| Feedback Network | Consists of resistors that provide feedback to the op-amp, ensuring the circuit maintains the desired current output. |
| Power Supply | Provides the necessary voltage to power the op-amp and other components in the circuit. |
Operation of the Circuit
The operation of a precision current source op-amp circuit is based on the principle of negative feedback. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
- The op-amp compares the voltage at its inverting input (-) to the voltage at its non-inverting input (+).
- The feedback network adjusts the voltage at the inverting input to match the voltage at the non-inverting input.
- This adjustment ensures that the voltage difference between the inputs is zero, which in turn maintains a constant current through the circuit.
- The current through the resistor is determined by Ohm’s Law: I = V/R, where I is the current, V is the voltage across the resistor, and R is the resistance.
Applications of the Circuit
A precision current source op-amp circuit finds applications in various fields:
-
Data Acquisition Systems: These circuits are used to convert analog signals into digital signals for processing by a computer. The precision current source ensures accurate conversion.
-
Precision Measurement Circuits: In applications requiring high accuracy, such as scientific research and industrial control systems, these circuits are essential for maintaining consistent and reliable measurements.
-
Power Supplies: Precision current sources can be used to regulate the output current of power supplies, ensuring stable and accurate power delivery.
Design Considerations
When designing a precision current source op-amp circuit, several factors must be considered:
-
Op-Amp Selection: Choose an op-amp with high input impedance, low output impedance, and high gain bandwidth product to ensure stable operation.
-
Resistor Values: Select resistors with high precision and low temperature coefficient to maintain accuracy over a wide range of temperatures.
-
Power Supply: Use a stable and clean power supply to minimize noise and ensure accurate operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a precision current source op-amp circuit is a versatile and essential component in the field of analog electronics. By understanding its basics, components, operation, and applications, you can effectively design and implement these circuits in various projects. Whether you’re working on data acquisition systems, precision measurement circuits, or power supplies, a precision current source op-amp circuit is a valuable tool to have in your arsenal.
