Rail-to-Rail Op Amp Schematic: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), the term “rail-to-rail” refers to an amplifier’s ability to output signals that swing from the negative supply voltage to the positive supply voltage. This feature is highly desirable in many applications, as it allows for a wider range of signal processing. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of rail-to-rail op-amps, their schematics, and their applications.
Understanding Rail-to-Rail Op Amps
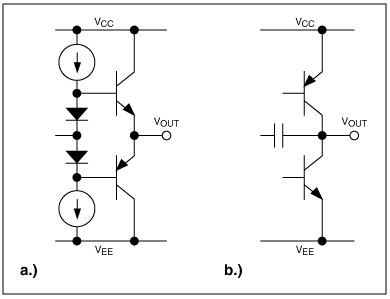
Rail-to-rail op-amps are designed to provide a wider output voltage range than traditional op-amps. This is achieved by using a push-pull output stage, which allows the output voltage to swing close to both the positive and negative supply voltages. As a result, rail-to-rail op-amps can amplify signals that are close to the supply voltages, which is particularly useful in applications where the signal range is limited.
One of the key advantages of rail-to-rail op-amps is their ability to provide a higher output current. This is because the push-pull output stage can deliver more current to the load, which is essential in applications that require high output power, such as audio amplifiers.
Components of a Rail-to-Rail Op Amp Schematic
A typical rail-to-rail op amp schematic consists of several key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Stage | Consists of differential input transistors that amplify the difference between the two input voltages. |
| Gain Stage | Increases the voltage gain of the op-amp by using a voltage follower configuration. |
| Output Stage | Comprises a push-pull output stage that allows the output voltage to swing close to both the positive and negative supply voltages. |
| Feedback Network | Consists of resistors and capacitors that determine the closed-loop gain and stability of the op-amp. |
These components work together to provide the desired performance characteristics of a rail-to-rail op-amp.
Applications of Rail-to-Rail Op Amps
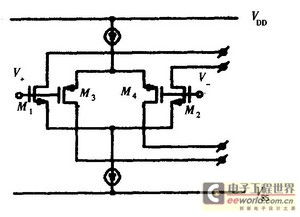
Rail-to-rail op-amps find applications in a wide range of fields, including audio amplifiers, signal conditioning, and data acquisition systems. Here are some of the key applications:
-
Audio Amplifiers: Rail-to-rail op-amps are commonly used in audio amplifiers due to their high output current and wide output voltage range. They can provide a clean and powerful audio signal, which is essential for high-quality audio reproduction.
-
Signal Conditioning: Rail-to-rail op-amps are used to condition signals in various applications, such as sensor interfacing, data acquisition, and communication systems. Their ability to amplify signals close to the supply voltages makes them ideal for these applications.
-
Data Acquisition Systems: Rail-to-rail op-amps are used in data acquisition systems to amplify and filter signals from sensors. Their high input impedance and low output impedance ensure that the signal is accurately captured and processed.
Choosing the Right Rail-to-Rail Op Amp
When selecting a rail-to-rail op-amp for a specific application, it is essential to consider several factors:
-
Supply Voltage Range: Ensure that the op-amp’s supply voltage range matches the requirements of your application.
-
Input Offset Voltage: Choose an op-amp with a low input offset voltage to minimize errors in your system.
-
Input Bias Current: Select an op-amp with a low input bias current to minimize loading effects on the input signal source.
-
Output Current: Choose an op-amp with a high output current to ensure sufficient power delivery to the load.
-
Power Consumption: Consider the power consumption of the op-amp, especially in battery-powered applications.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right rail-to-rail op-amp for your
