741 Op Amp Comparator Circuit: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the 741 op amp comparator circuit is essential for anyone delving into the world of analog electronics. This guide will walk you through the intricacies of this circuit, its components, and its applications. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how this circuit functions and its significance in various electronic systems.
Understanding the Basics
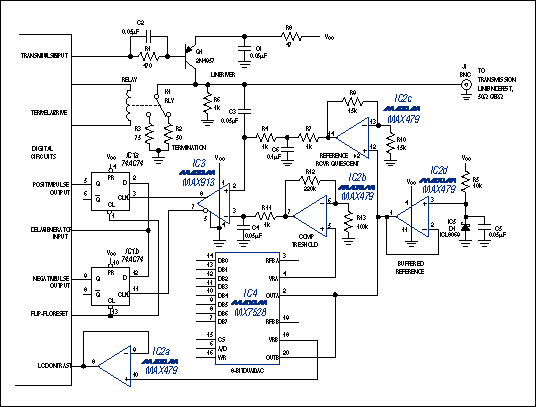
The 741 op amp comparator circuit is a fundamental building block in analog electronics. It compares two voltages and produces a digital output based on the comparison result. The circuit consists of an operational amplifier (op amp), a reference voltage, and two input voltages. The op amp amplifies the difference between the two input voltages, and the output is either high or low depending on which input voltage is higher.
Components of the 741 Op Amp Comparator Circuit

Here’s a breakdown of the key components in the 741 op amp comparator circuit:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) | The heart of the circuit, responsible for amplifying the difference between the two input voltages. |
| Reference Voltage | A fixed voltage level used for comparison with the input voltages. |
| Input Voltages | The voltages to be compared with the reference voltage. |
| Feedback Network | Used to set the gain of the op amp and determine the output voltage levels. |
How the Circuit Works
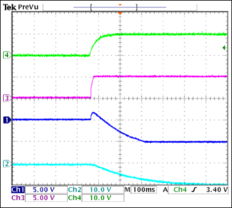
The 741 op amp comparator circuit operates as follows:
- The input voltages are applied to the non-inverting and inverting inputs of the op amp.
- The op amp amplifies the difference between the two input voltages.
- The amplified voltage is then compared with the reference voltage.
- The output of the op amp is either high or low, depending on which input voltage is higher.
Applications of the 741 Op Amp Comparator Circuit
The 741 op amp comparator circuit has a wide range of applications in various electronic systems. Some of the most common uses include:
- Threshold Detection: The circuit can be used to detect when an input voltage crosses a certain threshold level.
- Signal Conditioning: It can be used to convert analog signals into digital signals.
- Amplitude Comparison: The circuit can compare the amplitudes of two signals and produce a digital output based on the comparison.
- Window Comparator: It can be used to determine if an input voltage falls within a specific range.
Designing the 741 Op Amp Comparator Circuit
When designing a 741 op amp comparator circuit, there are several factors to consider:
- Input Offset Voltage: This is the voltage difference between the two input terminals when the inputs are at the same potential. It can affect the accuracy of the circuit, so it’s important to choose an op amp with a low input offset voltage.
- Input Bias Current: This is the current that flows into the input terminals of the op amp. It can cause errors in the circuit, so it’s important to choose an op amp with a low input bias current.
- Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR): This is the ability of the op amp to reject noise on the power supply lines. A high PSRR is desirable for a stable output.
Conclusion
The 741 op amp comparator circuit is a versatile and essential component in analog electronics. By understanding its components, operation, and applications, you can effectively utilize this circuit in various electronic systems. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, knowing how to design and implement the 741 op amp comparator circuit will undoubtedly enhance your skills in the field of analog electronics.
