Op Amp Integrator Filter: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the intricacies of electronic filters is crucial for anyone involved in signal processing. One such filter that stands out is the Op Amp Integrator. This article delves into the details of an Op Amp Integrator Filter, exploring its working principle, applications, and design considerations.
What is an Op Amp Integrator Filter?
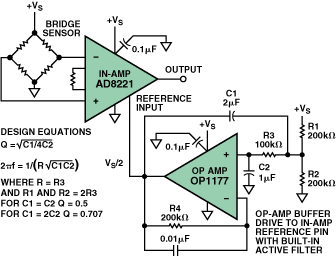
An Op Amp Integrator Filter is a type of electronic filter that uses an operational amplifier (op amp) to perform the mathematical operation of integration. It is widely used in various applications, including audio processing, control systems, and data acquisition.
Working Principle of an Op Amp Integrator Filter
The basic working principle of an Op Amp Integrator Filter involves the use of an op amp configured in an inverting configuration. The input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp, while the non-inverting input terminal is grounded. A resistor and a capacitor are connected in series between the output and the inverting input terminal.
When the input signal is applied, the op amp tries to maintain the voltage at its inverting input terminal equal to the voltage at its non-inverting input terminal, which is grounded. This results in the integration of the input signal, as the output voltage is proportional to the integral of the input voltage over time.
Applications of Op Amp Integrator Filters
Op Amp Integrator Filters find applications in various fields. Some of the common applications include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Audio Processing | Op Amp Integrator Filters are used in audio equipment to process signals, such as in reverb effects and audio equalizers. |
| Control Systems | They are used in control systems to process feedback signals and maintain stability. |
| Data Acquisition | Op Amp Integrator Filters are used in data acquisition systems to filter out noise and unwanted signals. |
Design Considerations for Op Amp Integrator Filters
Designing an Op Amp Integrator Filter requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance. Some of the key design considerations include:
-
Op Amp Selection: The choice of op amp is crucial, as it should have a wide bandwidth, low input offset voltage, and low noise.
-
Resistor and Capacitor Values: The values of the resistor and capacitor determine the cutoff frequency and the time constant of the filter. These values should be selected based on the desired filter characteristics.
-
Power Supply: The power supply voltage should be sufficient to provide the required output voltage swing and to ensure stable operation of the op amp.
-
Temperature Range: The filter should be designed to operate within the specified temperature range to ensure reliable performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Op Amp Integrator Filters
Like any other electronic component, Op Amp Integrator Filters have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Some of the key advantages include:
-
High Gain: Op Amp Integrator Filters offer high gain, which is essential for signal processing applications.
-
Low Distortion: They provide low distortion, ensuring accurate signal processing.
-
Wide Bandwidth: Op Amp Integrator Filters have a wide bandwidth, making them suitable for various applications.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
-
Input Offset Voltage: Op Amp Integrator Filters may suffer from input offset voltage, which can affect the accuracy of the filter.
-
Nonlinearities: Nonlinearities in the op amp can introduce distortion in the output signal.
-
Temperature Sensitivity: Op Amp Integrator Filters may be sensitive to temperature variations, which can affect their performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Op Amp Integrator Filter is a versatile and powerful tool in electronic signal processing. By understanding its working principle, applications, and design considerations, you can effectively utilize this filter in various projects. Whether you are working on audio processing
