Understanding the Op Amp Buffer with Gain: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to amplifying signals in electronic circuits, the op amp buffer with gain is a fundamental building block. This versatile component not only serves as a buffer but also provides the necessary amplification to drive loads effectively. In this detailed guide, we will explore the intricacies of the op amp buffer with gain, its applications, and how it works.
What is an Op Amp Buffer with Gain?
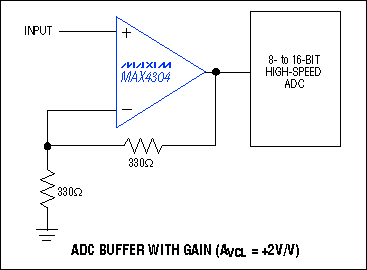
An op amp buffer with gain is a circuit configuration that combines the properties of an operational amplifier (op amp) and a buffer amplifier. The op amp provides the amplification, while the buffer ensures that the output signal is clean and free from loading effects.
Components of an Op Amp Buffer with Gain

The basic components of an op amp buffer with gain include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) | The core component that provides the amplification. |
| Feedback Resistor (Rf) | Connects the output of the op amp to its inverting input, determining the gain of the circuit. |
| Input Resistor (Ri) | Connects the input signal to the inverting input of the op amp. |
| Feedback Capacitor (Cf) | Optional component that can be used to filter out high-frequency noise. |
How Does an Op Amp Buffer with Gain Work?
The op amp buffer with gain operates based on the principle of negative feedback. The input signal is applied to the inverting input of the op amp, and the output signal is fed back to the inverting input through the feedback resistor (Rf). The gain of the circuit is determined by the ratio of Rf to Ri.
When the input signal is applied, the op amp amplifies it and drives the output. The amplified output signal is then fed back to the inverting input, which causes the op amp to adjust its output to maintain a virtual ground at the inverting input. This process ensures that the output signal is clean and free from loading effects.
Applications of Op Amp Buffer with Gain
The op amp buffer with gain finds applications in various electronic circuits, including:
- Signal conditioning: Amplifying weak signals for further processing.
- Impedance matching: Driving loads with high impedance.
- Filtering: Filtering out unwanted noise from the signal.
- Buffering: Isolating the input signal from the output signal.
Designing an Op Amp Buffer with Gain
When designing an op amp buffer with gain, consider the following factors:
- Input signal range: Ensure that the input signal is within the specified range of the op amp.
- Gain requirement: Determine the desired gain for the circuit.
- Power supply: Choose an appropriate power supply voltage for the op amp.
- Component selection: Select the appropriate resistors and capacitors for the desired gain and filtering requirements.
Advantages of Op Amp Buffer with Gain
The op amp buffer with gain offers several advantages, including:
- High gain: Provides the necessary amplification for weak signals.
- Low output impedance: Drives loads with high impedance effectively.
- High input impedance: Minimizes loading effects on the input signal.
- Low noise: Filters out unwanted noise from the signal.
Disadvantages of Op Amp Buffer with Gain
Despite its advantages, the op amp buffer with gain has some disadvantages, such as:
- Power consumption: The op amp consumes power, which may be a concern in battery-powered applications.
- Complexity: The circuit design can be complex, requiring careful component selection and layout.
- Temperature sensitivity: The performance of the op amp may be affected by temperature variations.
Conclusion
In conclusion
