Op Amp Based Comparators: A Comprehensive Guide
Op amp based comparators are essential components in electronic circuits, providing a straightforward way to compare two voltages. In this detailed guide, we will explore the various aspects of op amp comparators, including their working principle, types, applications, and design considerations.
Understanding Op Amp Based Comparators

Op amp comparators are designed to compare two input voltages and produce a digital output based on the comparison result. The basic principle is simple: if the non-inverting input voltage is higher than the inverting input voltage, the output is high; otherwise, it is low. This functionality makes op amp comparators ideal for various applications, such as signal detection, threshold detection, and analog-to-digital conversion.
Working Principle
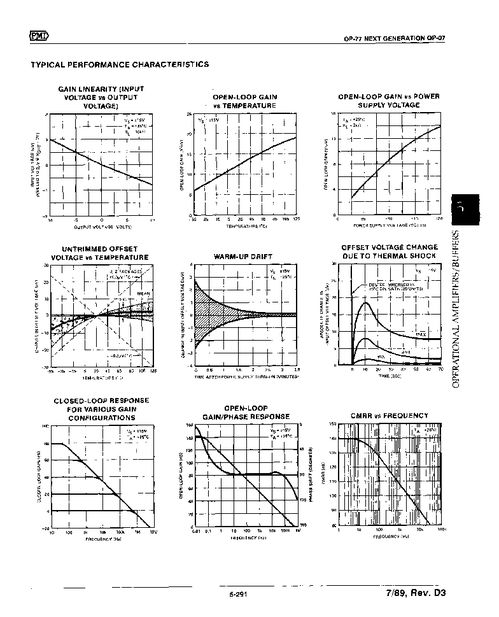
Op amp comparators work based on the open-loop gain of the operational amplifier. When the non-inverting input voltage is higher than the inverting input voltage, the op amp output goes to its positive supply voltage, and when the inverting input voltage is higher, the output goes to its negative supply voltage. The transition between these two states is very fast, typically in the order of nanoseconds.
Types of Op Amp Comparators
There are several types of op amp comparators, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Here are some of the most common types:
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold Comparator | Compares an input voltage to a reference voltage and produces a digital output based on the comparison result. | Signal detection, threshold detection, and analog-to-digital conversion. |
| Window Comparator | Compares an input voltage to a range of reference voltages and produces a digital output based on the comparison result. | Multi-level threshold detection, frequency measurement, and analog-to-digital conversion. |
| Zero-crossing Comparator | Detects the point where the input voltage crosses the zero voltage level and produces a digital output. | Signal processing, frequency measurement, and analog-to-digital conversion. |
Applications of Op Amp Comparators
Op amp comparators find applications in various fields, including:
- Signal detection and processing
- Threshold detection
- Analog-to-digital conversion
- Frequency measurement
- Power supply control
- Medical equipment
- Automotive systems
Design Considerations
When designing an op amp comparator circuit, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance:
- Input offset voltage: The difference between the two input voltages when the output is at its mid-point. A lower input offset voltage is desirable for better accuracy.
- Input bias current: The current flowing into the input terminals of the op amp. A lower input bias current is preferable for reducing the loading effect on the input signal.
- Output voltage swing: The range of output voltage levels that the comparator can produce. A wider output voltage swing is desirable for driving loads with varying requirements.
- Response time: The time taken by the comparator to switch from one state to another. A faster response time is preferable for applications requiring high-speed operation.
Conclusion
Op amp based comparators are versatile and essential components in electronic circuits. By understanding their working principle, types, applications, and design considerations, you can effectively utilize these devices in your projects. Whether you are working on signal detection, threshold detection, or analog-to-digital conversion, op amp comparators offer a reliable and efficient solution.
