Understanding the Voltage Follower Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered about the inner workings of the voltage follower operational amplifier (op amp)? This versatile component is widely used in various electronic circuits due to its unique characteristics. In this article, we will delve into the details of the voltage follower op amp, exploring its functionality, applications, and advantages. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and learn more about this fascinating electronic device.
What is a Voltage Follower Op Amp?
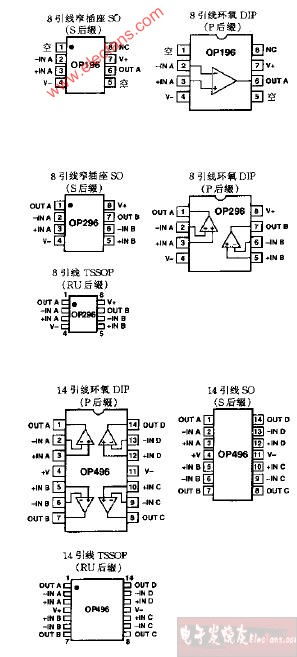
A voltage follower op amp, also known as a unity gain buffer, is an electronic circuit that amplifies the input voltage by a factor of one. It is designed to have a very high input impedance and a very low output impedance, ensuring that the output voltage follows the input voltage with minimal distortion. The voltage follower op amp is often represented by the symbol

How Does a Voltage Follower Op Amp Work?
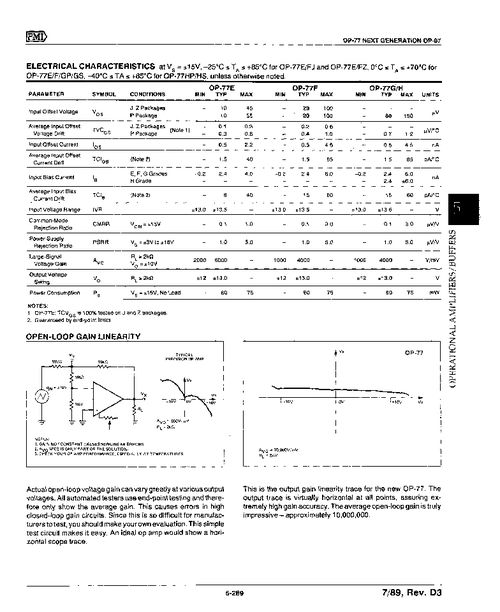
The voltage follower op amp operates based on the principle of negative feedback. The input voltage is applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp, while the non-inverting input terminal is connected to ground. The output voltage is then fed back to the inverting input terminal through a resistor, creating a closed-loop feedback system. This configuration ensures that the voltage at the inverting input terminal is held at zero, resulting in a voltage gain of one.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how a voltage follower op amp works:
- The input voltage is applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp.
- The op amp compares the voltage at the inverting input terminal with the voltage at the non-inverting input terminal (which is grounded).
- The difference between the two voltages is amplified by the op amp’s open-loop gain.
- The amplified voltage is then fed back to the inverting input terminal through a resistor.
- The op amp adjusts its output voltage to minimize the difference between the inverting and non-inverting input terminals, resulting in a voltage gain of one.
Applications of the Voltage Follower Op Amp
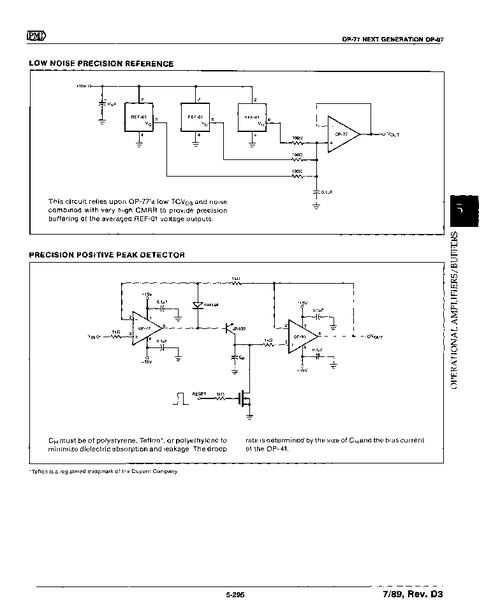
The voltage follower op amp has numerous applications in electronic circuits. Some of the most common uses include:
- Buffering: The high input impedance and low output impedance of the voltage follower op amp make it an ideal buffer for driving loads with high impedance, such as long cables or sensitive electronic devices.
- Impedance matching: The voltage follower op amp can be used to match the input impedance of a circuit to the output impedance of another circuit, ensuring optimal signal transfer.
- Signal isolation: By using a voltage follower op amp, you can isolate two circuits from each other, preventing any interference or noise from affecting the signal.
- Level shifting: The voltage follower op amp can be used to shift the voltage level of a signal, making it compatible with different electronic devices or circuits.
Advantages of the Voltage Follower Op Amp
There are several advantages to using a voltage follower op amp in electronic circuits:
- High input impedance: The voltage follower op amp has a very high input impedance, which means it draws minimal current from the input signal source.
- Low output impedance: The voltage follower op amp has a very low output impedance, which ensures that the output signal is stable and unaffected by the load.
- Unity gain: The voltage follower op amp provides a voltage gain of one, making it an ideal buffer for driving loads with high impedance.
- Wide bandwidth: The voltage follower op amp has a wide bandwidth, allowing it to handle a wide range of frequencies without distortion.
Choosing the Right Voltage Follower Op Amp
When selecting a voltage follower op amp for your circuit, there are several factors to consider:
- Supply voltage: Ensure that the op amp’s supply voltage range is compatible with your circuit’s voltage requirements.
- Input offset voltage: Choose an op amp with a low input offset voltage to minimize errors in your circuit.
-
