Op Amp Layout: A Comprehensive Guide for Designers
When it comes to designing circuits, the operational amplifier (op amp) layout is a crucial component that can significantly impact the performance and functionality of your circuit. In this detailed guide, we will explore the various aspects of op amp layout, including its importance, different types, and best practices for designing an effective layout.
Understanding the Basics of Op Amp Layout
Before diving into the specifics of op amp layout, it’s essential to understand what an op amp is and how it functions. An op amp is an electronic device that amplifies the difference between two input voltages and produces an output voltage that is proportional to the input difference. It is widely used in various applications, such as signal conditioning, filtering, and amplification.
Op amp layout refers to the arrangement of the op amp and its associated components on a printed circuit board (PCB). A well-designed op amp layout can minimize noise, improve stability, and enhance the overall performance of the circuit.
Importance of Op Amp Layout
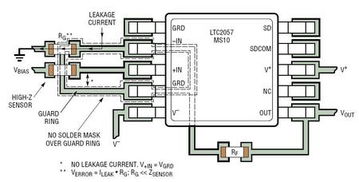
Several factors make op amp layout crucial for circuit design:
-
Minimizing Noise: A well-designed layout can reduce noise interference, ensuring that the circuit operates accurately and reliably.
-
Improving Stability: Proper layout can prevent oscillations and instability, which can lead to circuit failure.
-
Enhancing Performance: An optimized layout can improve the circuit’s bandwidth, gain, and other critical parameters.
-
Reducing Cost: A well-designed layout can minimize the number of components and traces, reducing the overall cost of the circuit.
Types of Op Amp Layouts
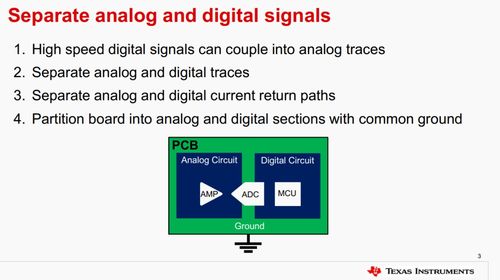
There are several types of op amp layouts, each with its unique characteristics and applications:
Single-Ended Layout
The single-ended layout is the most common type of op amp layout. It consists of an op amp with one input and one output. This layout is suitable for applications where the input signal is unbalanced, such as audio amplifiers and signal conditioning circuits.
Differential Layout
The differential layout uses two op amps to amplify the difference between two input signals. This type of layout is ideal for applications that require high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), such as data acquisition systems and communication circuits.
Bridge Layout
The bridge layout is a variation of the differential layout, where the two input signals are applied to the non-inverting inputs of the op amps. This configuration is commonly used in precision measurement and sensor applications.
Best Practices for Op Amp Layout
Designing an effective op amp layout requires attention to detail and adherence to certain best practices:
-
Keep Traces Short and Direct: Minimize the length of traces between the op amp and its associated components to reduce noise and improve signal integrity.
-
Use Proper Power Supply Decoupling: Implement decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins of the op amp to filter out noise and ensure stable power supply.
-
Minimize Loop Area: Reduce the loop area around the op amp to minimize the effect of magnetic fields and reduce noise.
-
Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Adhere to the layout guidelines provided by the op amp manufacturer to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, op amp layout is a critical aspect of circuit design that can significantly impact the performance and functionality of your circuit. By understanding the basics of op amp layout, the different types of layouts, and best practices for designing an effective layout, you can create circuits that are more reliable, accurate, and cost-effective.
| Op Amp Layout Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Ended Layout | Consists of an op amp with one input and one output | Audio amplifiers, signal conditioning circuits |
| Differential Layout | Uses two op amps to amplify the difference between two input signals | Data acquisition systems, communication circuits |
| Bridge Layout | function pinIt() { var e = document.createElement('script'); e.setAttribute('type','text/javascript'); e.setAttribute('charset','UTF-8'); e.setAttribute('src','https://assets.pinterest.com/js/pinmarklet.js?r='+Math.random()*99999999); document.body.appendChild(e); }
