Op Amp Rails: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to understanding operational amplifiers (op amps), one of the most crucial components to consider is the op amp rails. These are the power supply voltages that determine the performance and functionality of the op amp. In this article, we will delve into the details of op amp rails, their significance, and how they affect the overall performance of an op amp circuit.
What are Op Amp Rails?
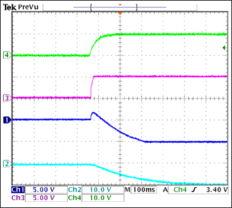
Op amp rails refer to the power supply voltages that an op amp operates from. These voltages are typically represented as positive and negative values, such as +15V and -15V. The rail voltages are essential for the op amp to function correctly and provide the desired output.
Op amp rails are usually provided by a power supply unit (PSU) that delivers a stable and regulated voltage. The PSU should be capable of providing the required voltage levels and current to ensure the op amp operates within its specified parameters.
Significance of Op Amp Rails
The op amp rails play a critical role in determining the performance of an op amp circuit. Here are some key aspects where op amp rails are significant:
-
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range: The input common-mode voltage range is the range of voltages at which the op amp can operate without distortion. This range is determined by the op amp rails. If the input voltage exceeds the common-mode voltage range, the op amp may produce incorrect output or even damage itself.
-
Output Voltage Swing: The output voltage swing of an op amp is the range of voltages it can produce between its output terminals. This range is also influenced by the op amp rails. A wider rail voltage allows for a larger output voltage swing, which can be beneficial in certain applications.
-
Power Consumption: The power consumption of an op amp is directly related to the rail voltages. Higher rail voltages can lead to increased power consumption, which may affect the overall efficiency of the circuit.
-
Stability: The stability of an op amp circuit is crucial for accurate and reliable performance. Op amp rails contribute to the stability of the circuit by providing a stable power supply, which helps minimize noise and distortion.
Types of Op Amp Rails
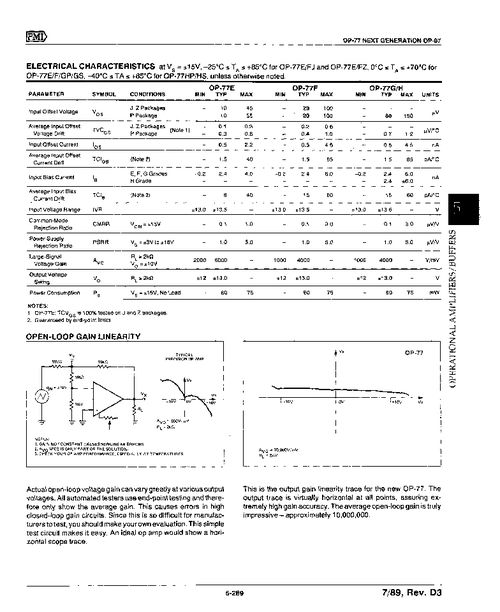
There are various types of op amp rails, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some common types:
-
Single Rail: A single rail power supply provides a single voltage rail, either positive or negative. This type of rail is commonly used in battery-powered applications or when a single supply voltage is sufficient for the circuit.
-
Split Rail: A split rail power supply provides both positive and negative voltage rails. This type of rail is commonly used in applications that require a wide input common-mode voltage range or a large output voltage swing.
-
杞ㄥ杞紙Rail-to-Rail锛?杞ㄥ杞ㄧ數婧愭彁渚涙帴杩戠數婧愯建鐨勮緭鍑虹數鍘嬶紝杩欐剰鍛崇潃杈撳嚭鐢靛帇鍙互鎺ヨ繎姝h礋鐢垫簮杞ㄣ€傝繖绉嶇數婧愬湪闇€瑕侀珮杈撳嚭鐢靛帇鎽嗗箙鐨勫簲鐢ㄤ腑闈炲父鏈夌敤銆?/p>
Choosing the Right Op Amp Rails
Selecting the appropriate op amp rails is crucial for achieving optimal performance in an op amp circuit. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right op amp rails:
-
Application Requirements: Understand the specific requirements of your application, such as the input common-mode voltage range, output voltage swing, and power consumption. This will help you determine the appropriate rail voltages.
-
Op Amp Specifications: Refer to the op amp’s datasheet to find the recommended rail voltages. The datasheet will provide information on the minimum and maximum rail voltages required for optimal performance.
-
Power Supply Stability: Ensure that the power supply can provide a stable and regulated voltage to the op amp. This is crucial for minimizing noise and distortion in the circuit.
-
Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the power supply components. Sometimes, using a standard power supply configuration may be more cost-effective and easier to implement.
