Understanding the Op-Amp Comparator: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered how an op-amp comparator works? This versatile electronic component is widely used in various applications, from simple threshold detection to complex signal processing. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the op-amp comparator, exploring its working principle, types, advantages, and applications. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and unravel the mysteries of the op-amp comparator.
What is an Op-Amp Comparator?
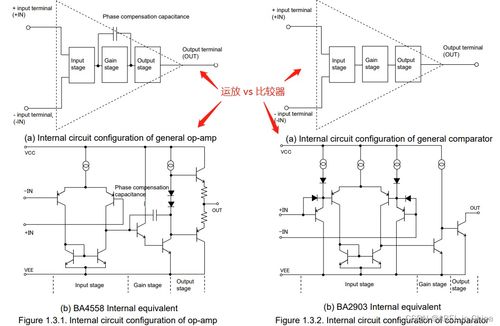
An op-amp comparator is a device that compares two input voltages and produces an output voltage that indicates which input voltage is higher. It is essentially a voltage comparator, which uses an operational amplifier (op-amp) as its core component. The op-amp comparator operates on the principle of open-loop gain, where the output voltage is directly proportional to the difference between the two input voltages.
Working Principle of an Op-Amp Comparator
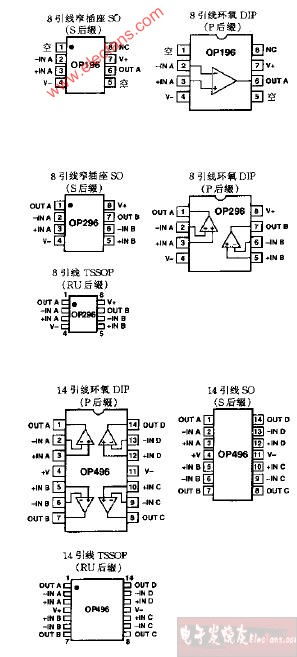
The working principle of an op-amp comparator is based on the open-loop gain of the op-amp. When the non-inverting input (+) is higher than the inverting input (-), the output voltage is at its maximum positive value. Conversely, when the inverting input is higher than the non-inverting input, the output voltage is at its maximum negative value. The output voltage is determined by the voltage difference between the two inputs and the open-loop gain of the op-amp.
Here’s a simplified representation of the working principle:
| Input Voltage Difference (Vd) | Output Voltage (Vo) |
|---|---|
| Vd > 0 | Vo = Vsat+ (Maximum Positive Output) |
| Vd < 0 | Vo = Vsat- (Maximum Negative Output) |
Types of Op-Amp Comparators

There are several types of op-amp comparators, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common types:
- Single Supply Comparator: This type of comparator operates with a single supply voltage and requires a reference voltage for proper operation.
- Differential Input Comparator: It compares the voltage difference between two input terminals, making it suitable for applications where common-mode noise is a concern.
- Window Comparator: This comparator has two reference voltages and produces an output when the input voltage falls within a specific range (window). It is commonly used in temperature sensing applications.
- Threshold Comparator: It generates an output when the input voltage crosses a predefined threshold value. This type of comparator is widely used in digital signal processing and communication systems.
Advantages of Op-Amp Comparators
Op-amp comparators offer several advantages that make them indispensable in various applications:
- High Input Impedance: Op-amp comparators have a high input impedance, which means they draw minimal current from the input signal source.
- Low Output Impedance: They provide a low output impedance, ensuring that the output signal can drive loads with minimal distortion.
- High Speed: Op-amp comparators can operate at high speeds, making them suitable for applications that require rapid response times.
- Low Power Consumption: They consume minimal power, which is crucial for battery-powered devices.
Applications of Op-Amp Comparators
Op-amp comparators find applications in a wide range of fields, including:
- Signal Processing: They are used for signal conditioning, filtering, and amplification in various signal processing applications.
- Communication Systems: Op-amp comparators are used in communication systems for signal detection, demodulation, and encoding.
- Medical Devices: They are employed in medical devices for measuring and monitoring physiological signals, such as heart rate and blood pressure.
- Consumer Electronics: Op-amp comparators are used in consumer electronics for audio processing, image processing, and sensor interfacing.
In conclusion, the
