Buffer Amplifier Op-Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the buffer amplifier operational amplifier (op-amp) is crucial for anyone delving into the world of electronics. This guide will walk you through the intricacies of this essential component, covering its functionality, applications, and key specifications. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, this article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the buffer amplifier op-amp.
What is a Buffer Amplifier Op-Amp?
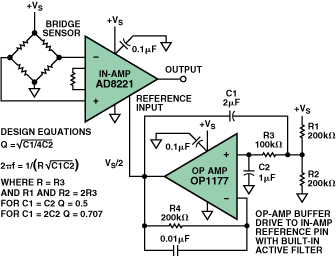
A buffer amplifier op-amp is a type of operational amplifier designed to provide high input impedance and low output impedance. It acts as a voltage buffer, maintaining the input voltage while driving a low-impedance load. This feature makes it an indispensable component in various electronic circuits.
Functionality of a Buffer Amplifier Op-Amp

The primary function of a buffer amplifier op-amp is to isolate the input signal from the output load. This isolation ensures that the input signal remains unaffected by the load, allowing for accurate signal transmission. Here’s a breakdown of its key functionalities:
-
High Input Impedance: The buffer amplifier op-amp has a high input impedance, which means it draws minimal current from the input signal source. This characteristic ensures that the input signal remains unchanged.
-
Low Output Impedance: The buffer amplifier op-amp has a low output impedance, which allows it to drive low-impedance loads without affecting the signal quality.
-
Signal Isolation: The buffer amplifier op-amp isolates the input signal from the output load, ensuring that the signal remains unaffected by the load.
-
High Gain: While not always required, buffer amplifier op-amps can provide high gain, which is useful in certain applications.
Applications of Buffer Amplifier Op-Amp
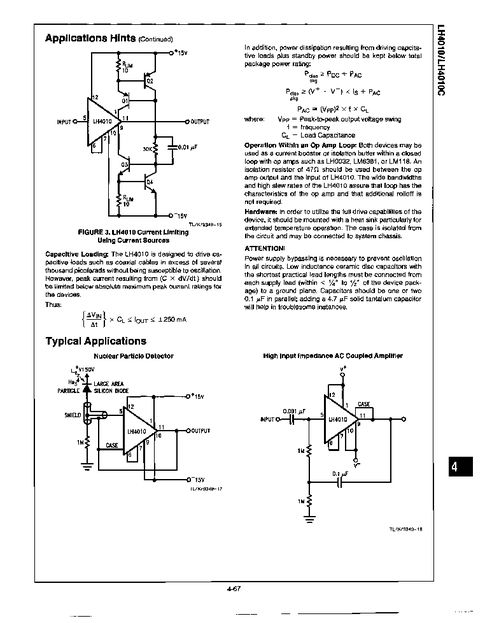
Buffer amplifier op-amps find applications in a wide range of electronic circuits. Here are some common examples:
-
Signal Isolation: Buffer amplifier op-amps are used to isolate sensitive input signals from high-impedance loads, such as in audio and video circuits.
-
Impedance Matching: They are used to match the input impedance of a circuit to the output impedance of a signal source, ensuring optimal signal transfer.
-
Signal Buffering: Buffer amplifier op-amps are used to buffer signals in various stages of a circuit, ensuring that the signal remains strong and unaffected by the load.
-
Amplification: In some cases, buffer amplifier op-amps can provide additional amplification to weak signals.
Key Specifications of Buffer Amplifier Op-Amp
When selecting a buffer amplifier op-amp for your circuit, it’s essential to consider its key specifications. Here are some of the most important ones:
-
Input Impedance: The input impedance of a buffer amplifier op-amp should be high enough to minimize the loading effect on the input signal source.
-
Output Impedance: The output impedance of a buffer amplifier op-amp should be low enough to drive low-impedance loads without affecting the signal quality.
-
Gain: While not always required, the gain of a buffer amplifier op-amp should be sufficient for your application.
-
Power Supply Voltage: The power supply voltage of a buffer amplifier op-amp should be compatible with your circuit’s requirements.
-
Bandwidth: The bandwidth of a buffer amplifier op-amp should be wide enough to accommodate the frequency range of your application.
Comparison of Different Buffer Amplifier Op-Amp Types
There are several types of buffer amplifier op-amps available, each with its unique characteristics. Here’s a comparison of some popular types:
| Type | Input Impedance | Output Impedance | Gain | Power Supply Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Op-Amp with Internal Compensation | High | Low | Variable |
function pinIt()
{
var e = document.createElement('script');
e.setAttribute('type','text/javascript');
e.setAttribute('charset','UTF-8');
e.setAttribute('src','https://assets.pinterest.com/js/pinmarklet.js?r='+Math.random()*99999999);
document.body.appendChild(e);
}
|
