Understanding Op Amp Difference: A Comprehensive Guide
Operational amplifiers, or op amps, are fundamental components in electronic circuits. They are used in a wide range of applications, from audio amplification to signal processing. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of op amp difference, exploring its various aspects and how it impacts circuit design.
What is an Op Amp Difference?
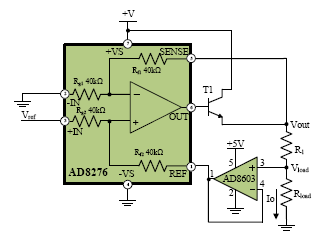
An op amp difference refers to the difference in voltage between the two input terminals of an operational amplifier. This difference is crucial in determining the output voltage of the op amp. Understanding how this difference works is essential for designing circuits that rely on op amps.
Types of Op Amps

There are several types of op amps available in the market, each with its own set of characteristics. The most common types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Single-supply | Operates with a single supply voltage, eliminating the need for a negative supply rail. |
| Differential-input | Accepts differential input signals, which are the difference between two input voltages. |
| Low-power | Designed for low-power applications, making them suitable for battery-powered devices. |
| High-speed | Capable of operating at high frequencies, making them suitable for signal processing applications. |
Op Amp Difference in Circuit Design

Op amp difference plays a vital role in circuit design. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Input Offset Voltage: The input offset voltage is the voltage difference between the two input terminals when the output is at zero. This voltage can cause errors in the circuit, so it is important to choose an op amp with a low input offset voltage.
2. Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): The CMRR is a measure of an op amp’s ability to reject common-mode signals. A high CMRR ensures that the circuit is less susceptible to noise and interference.
3. Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR): The PSRR is a measure of an op amp’s ability to reject power supply noise. A high PSRR ensures that the circuit’s performance is not affected by fluctuations in the power supply voltage.
Op Amp Difference in Practical Applications
Op amp difference is essential in various practical applications, such as:
1. Signal Amplification: Op amps are widely used for amplifying signals in audio and communication systems. The difference in voltage between the input terminals determines the amplification factor.
2. Signal Filtering: Op amps can be used to design filters that remove unwanted noise and interference from signals. The difference in voltage helps in determining the cutoff frequency of the filter.
3. Analog-to-Digital Conversion: Op amps are used in analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) to convert analog signals into digital values. The difference in voltage is crucial in determining the accuracy of the conversion.
Op Amp Difference in Circuit Simulation
Circuit simulation tools, such as SPICE, can be used to analyze the behavior of op amp circuits. By simulating the op amp difference, designers can predict the performance of the circuit under various conditions.
1. Transient Analysis: Transient analysis helps in understanding the behavior of the circuit over time. By simulating the op amp difference, designers can observe how the circuit responds to changes in input voltage.
2. AC Analysis: AC analysis helps in understanding the frequency response of the circuit. By simulating the op amp difference, designers can determine the circuit’s bandwidth and stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, op amp difference is a crucial aspect of op amp design and circuit analysis. Understanding how it works and its impact on circuit performance is essential for designing reliable and efficient electronic circuits.
