Op Amp LFO Circuit Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Op Amp LFO circuit diagram is essential for anyone interested in audio synthesis and signal processing. This guide will delve into the intricacies of this circuit, providing you with a detailed understanding of its components, operation, and applications.
Understanding the Basics
The Op Amp LFO, or Operational Amplifier Low-Frequency Oscillator, is a versatile circuit used to generate low-frequency oscillating signals. It is widely employed in various audio applications, including synthesizers, effects processors, and musical instruments. The heart of this circuit is the operational amplifier, which serves as the core component responsible for amplifying and shaping the signal.
Components of the Op Amp LFO Circuit
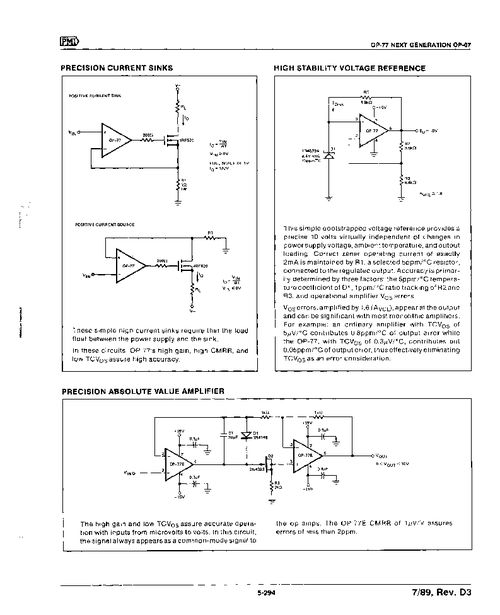
The Op Amp LFO circuit typically consists of the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) | The main component responsible for amplifying and shaping the signal. |
| Resistors | Used to control the gain, frequency, and other parameters of the oscillator. |
| Capacitors | Used to determine the frequency of the oscillator and to filter the signal. |
| Diodes | Used to create non-linear characteristics in the signal, which can be useful for creating more complex waveforms. |
These components work together to generate a stable, low-frequency oscillating signal that can be used in various applications.
Operation of the Op Amp LFO Circuit

The Op Amp LFO circuit operates based on the principle of negative feedback. The operational amplifier amplifies the input signal and then feeds it back to the inverting input, which reduces the overall gain. This process creates a stable oscillating signal with a frequency determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the Op Amp LFO circuit operates:
- The input signal is applied to the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier.
- The operational amplifier amplifies the input signal and then feeds it back to the inverting input through a resistor and capacitor network.
- The resistor and capacitor network determines the frequency of the oscillating signal.
- The operational amplifier compares the amplified signal with the feedback signal and adjusts the output accordingly to maintain a stable oscillation.
Applications of the Op Amp LFO Circuit
The Op Amp LFO circuit has a wide range of applications in audio synthesis and signal processing. Some of the most common uses include:
- Generating low-frequency oscillating signals for synthesizers and effects processors.
- Creating LFOs for modulating various parameters, such as pitch, volume, and filter cutoff frequencies.
- Designing complex waveforms by combining multiple LFOs and other signal processing techniques.
Building Your Own Op Amp LFO Circuit
Building your own Op Amp LFO circuit can be a rewarding and educational experience. To get started, you’ll need the following components:
- Operational Amplifier (Op Amp)
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Diodes
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
- Soldering Iron and Solder
Follow these steps to build your own Op Amp LFO circuit:
- Design the circuit layout on your PCB, ensuring that the components are placed correctly and that the traces are well-organized.
- Solder the components to the PCB, following the circuit diagram as a reference.
- Connect the power supply to the circuit and test the output using an oscilloscope or audio analyzer.
- Tune the circuit by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors to achieve the desired frequency and waveform.
Building your own Op Amp LFO circuit can provide you with a deeper understanding of the circuit’s operation and allow you to customize it to
