Understanding VP Shunt Post-Op Nursing Care

When a patient undergoes a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt surgery, the role of the nursing care team becomes crucial. This article aims to provide a detailed and multi-dimensional introduction to the post-operative nursing care for VP shunt patients.
What is a VP Shunt?
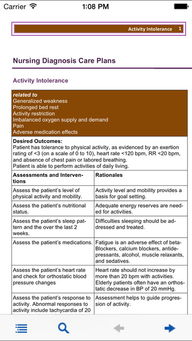
A VP shunt is a surgically placed device that helps to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain to the abdomen or chest. This fluid is produced by the brain and circulates around it, and in some cases, it can accumulate and cause increased intracranial pressure (ICP). The shunt helps to alleviate this pressure and prevent complications such as brain damage or stroke.
Post-Op Nursing Care: The Initial Hours
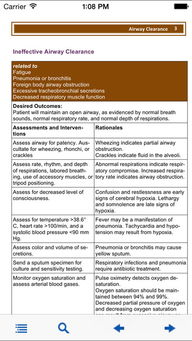
After the surgery, the patient will be closely monitored in the recovery room. The following are some key aspects of post-op nursing care:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitoring Vital Signs | Regularly check the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature to ensure stability. |
| Head Positioning | Maintain the patient’s head in an elevated position to reduce intracranial pressure. |
| IV Fluids and Medications | Administer IV fluids and medications as prescribed by the physician to manage pain, prevent infection, and maintain hydration. |
| Wound Care | Keep the surgical site clean and dry, and monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. |
Monitoring for Complications
One of the most critical aspects of post-op nursing care is monitoring for complications. Some common complications include:
-
CSF Leak: Look for signs of CSF leak, such as clear fluid draining from the incision site or a decrease in urine output.
-
Infection: Monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or fever.
-
Obstruction: Watch for signs of shunt obstruction, such as increased intracranial pressure, headache, or changes in consciousness.
-
Shunt Malfunction: Be aware of signs of shunt malfunction, such as sudden changes in the patient’s condition, increased intracranial pressure, or shunt malfunction.
Education and Support
Education and support are essential components of post-op nursing care. The following are some key areas to focus on:
-
Understanding the Shunt: Explain how the shunt works, its purpose, and the importance of maintaining it.
-
Activity Restrictions: Advise the patient on activity restrictions, such as avoiding heavy lifting or straining.
-
Medication Management: Educate the patient on the importance of taking medications as prescribed and the potential side effects.
-
Follow-Up Appointments: Schedule follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider to monitor the patient’s recovery and address any concerns.
Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration between the nursing care team, the patient, and the healthcare provider are crucial for successful post-op nursing care. This includes:
-
Regular Updates: Keep the patient and their family informed about the patient’s condition and progress.
-
Addressing Concerns: Listen to the patient’s concerns and address them promptly.
-
Collaboration with Other Healthcare Providers: Work closely with other healthcare providers, such as neurosurgeons, neurologists, and physical therapists, to ensure the best possible care for the patient.
Conclusion
Post-op nursing care for VP shunt patients is a complex and multifaceted process. By focusing on monitoring for complications, providing education and support, and maintaining effective communication and collaboration, the nursing care team can help ensure the best possible outcome for the patient.
