Rail to Rail Precision Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), the term “rail to rail” refers to a crucial feature that can significantly impact the performance of your circuit. In this article, we will delve into the details of rail-to-rail precision op-amps, exploring their characteristics, applications, and benefits. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of what makes these op-amps stand out from their counterparts.
Understanding Rail-to-Rail Precision Op Amps
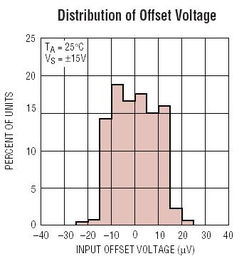
Rail-to-rail precision op-amps are designed to operate with input and output voltages that span the full range between the positive and negative supply voltages. This means that the output voltage can swing all the way to the supply voltage rails, providing a wider dynamic range and improved performance in various applications.
Let’s take a closer look at some key characteristics of rail-to-rail precision op-amps:
| Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | Spans the full range between the positive and negative supply voltages |
| Output Voltage Range | Swings all the way to the supply voltage rails |
| Low Offset Voltage | Minimizes errors in the output voltage due to the input offset voltage |
| Low Input Bias Current | Reduces the loading effect on the input signal source |
| High Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) | Improves the accuracy of the op-amp’s output by rejecting common-mode noise |
| Low Power Consumption | Enhances the efficiency of the circuit |
Applications of Rail-to-Rail Precision Op Amps
Rail-to-rail precision op-amps find applications in a wide range of circuits and systems. Some of the most common applications include:
- Audio amplifiers
- Signal conditioning circuits
- Instrumentation amplifiers
- Power supply monitoring circuits
- Medical equipment
- Wireless communication systems
Let’s explore some of these applications in more detail:
Audio Amplifiers
In audio amplifiers, rail-to-rail precision op-amps are used to amplify low-level audio signals while maintaining high fidelity. Their ability to swing close to the supply voltage rails ensures that the output signal has a wide dynamic range, resulting in better sound quality.
Signal Conditioning Circuits
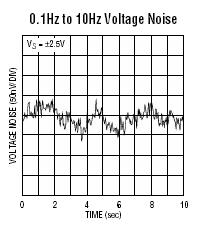
Signal conditioning circuits often require high precision and low noise. Rail-to-rail precision op-amps are ideal for these applications due to their low offset voltage, low input bias current, and high CMRR. They can be used to amplify, filter, and shape signals, ensuring accurate and reliable processing.
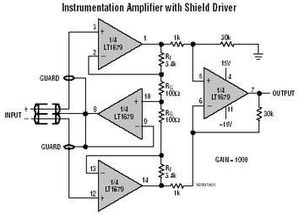
Instrumentation Amplifiers
Instrumentation amplifiers are used to amplify weak signals from sensors and transducers. Rail-to-rail precision op-amps provide the necessary precision and stability required for accurate measurements. Their wide input and output voltage ranges make them suitable for a variety of applications, including temperature, pressure, and strain measurements.
Power Supply Monitoring Circuits
Power supply monitoring circuits are essential for ensuring the stability and reliability of electronic systems. Rail-to-rail precision op-amps can be used to monitor and control the voltage levels of power supplies, protecting the system from overvoltage and undervoltage conditions.
Medical Equipment
In the medical field, rail-to-rail precision op-amps are used in various applications, such as patient monitoring systems, medical imaging devices, and diagnostic equipment. Their high precision and low noise characteristics ensure accurate and reliable measurements, contributing to better patient care.
Wireless Communication Systems
Wireless communication systems require high-performance op-amps for signal processing and transmission. Rail-to-rail precision op-amps offer the necessary precision, low noise, and wide dynamic range to meet the stringent requirements of these systems
