OPS: A Comprehensive Guide to Baseball’s On-Base Plus Slugging Statistic
When it comes to evaluating a baseball player’s offensive prowess, one of the most widely used metrics is OPS, which stands for On-Base Plus Slugging. This statistic combines two key components of a player’s offensive game: on-base percentage and slugging percentage. By understanding how OPS works and its significance, you can gain a deeper insight into a player’s overall offensive contribution to their team.
Understanding On-Base Percentage (OBP)
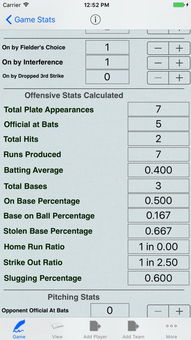
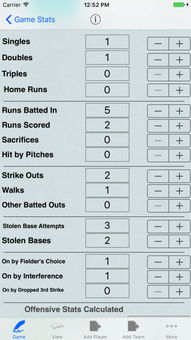
On-base percentage measures how often a player reaches base through hits, walks, and hit by pitches. It is calculated by dividing the total number of bases a player has reached by the sum of their at-bats, walks, hit by pitches, and sacrifices. A higher OBP indicates that a player is more likely to get on base, which can lead to more opportunities to score runs.
| Player | OBP | At-Bats | Walks | Hit by Pitches | Sacrifices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Player A | 0.400 | 500 | 50 | 10 | 5 |
| Player B | 0.300 | 500 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
Understanding Slugging Percentage (SLG)

Slugging percentage measures a player’s power at the plate, focusing on the number of extra-base hits they accumulate. It is calculated by dividing the total number of bases a player has driven in by the sum of their at-bats. A higher SLG indicates that a player is more likely to hit for extra bases, which can lead to more runs scored.
| Player | SLG | At-Bats | Home Runs | Doubles | Triples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Player A | 0.600 | 500 | 20 | 30 | 5 |
| Player B | 0.500 | 500 | 15 | 25 | 5 |
Calculating OPS
Once you have a player’s OBP and SLG, you can calculate their OPS by simply adding the two percentages together. This will give you a single number that represents their overall offensive production. The higher the OPS, the better the player’s offensive contribution to their team.
| Player | OBP | SLG | OPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Player A | 0.400 | 0.600 | 1.000 |
| Player B | 0.300 | 0.500 | 0.800 |
Interpreting OPS
OPS can be used to compare players across different eras and leagues, as it takes into account both on-base and slugging abilities. A player with an OPS of 1.000 is considered to be an elite offensive talent, while a player with an OPS below 0.700 may be considered below average. Here are some general guidelines for interpreting OPS:
- OPS of 1.000 or higher
