Buffer with Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electronic circuits, the buffer with operational amplifier (op amp) is a fundamental component that plays a crucial role in signal processing. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this circuit, exploring its various aspects to help you understand its significance and applications.
Understanding the Basics
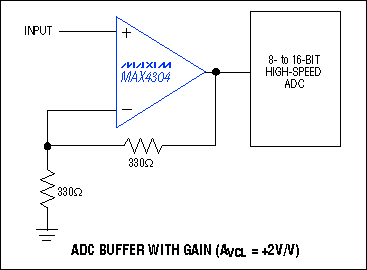
The buffer with op amp is designed to amplify a signal without changing its shape or frequency. It consists of an op amp and a feedback resistor network. The op amp amplifies the input signal, and the feedback resistor network determines the gain of the circuit.
One of the key advantages of using an op amp as a buffer is its high input impedance and low output impedance. This means that the buffer can drive loads with minimal loading effect on the source, making it an ideal choice for applications where signal integrity is crucial.
Types of Buffer Circuits

There are several types of buffer circuits, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common ones:
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Non-inverting Buffer | The input signal is applied to the non-inverting input terminal of the op amp, and the output is taken from the output terminal. | Signal amplification, impedance matching, and voltage follower applications |
| Inverting Buffer | The input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp, and the output is taken from the output terminal. | Signal inversion, impedance matching, and voltage follower applications |
| Non-inverting Summing Amplifier | Multiple input signals are applied to the non-inverting input terminal of the op amp, and the output is taken from the output terminal. | Signal mixing, signal addition, and voltage summation applications |
| Inverting Summing Amplifier | Multiple input signals are applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp, and the output is taken from the output terminal. | Signal mixing, signal subtraction, and voltage subtraction applications |
Designing a Buffer Circuit

Designing a buffer circuit involves selecting the appropriate op amp and feedback resistor network. Here are some key considerations:
- Op Amp Selection: Choose an op amp with high input impedance, low output impedance, and sufficient gain bandwidth product for your application.
- Feedback Resistor Network: The feedback resistor network determines the gain of the circuit. The gain is calculated as the ratio of the feedback resistor to the input resistor.
- Power Supply: Ensure that the op amp is powered with a suitable voltage supply to meet the required gain and output voltage levels.
Applications of Buffer Circuits
Buffer circuits find applications in a wide range of electronic systems, including:
- Audio Equipment: Buffers are used to drive speakers and headphones, ensuring that the signal is amplified without distortion.
- Telecommunications: Buffers are used to interface between different signal levels and impedance levels in telecommunication systems.
- Medical Equipment: Buffers are used in medical equipment to amplify and process physiological signals, such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electroencephalograms (EEGs).
- Industrial Control Systems: Buffers are used to interface between sensors and control systems, ensuring that the signal is accurately transmitted and processed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the buffer with op amp is a versatile and essential component in electronic circuits. Its ability to amplify signals without distortion and its high input impedance and low output impedance make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. By understanding the basics of buffer circuits and their design considerations, you can effectively implement these circuits in your projects.
