Differential Input Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the differential input operational amplifier (op amp) is crucial for anyone delving into the world of analog electronics. This guide will walk you through the intricacies of differential input op amps, their applications, and how they work. Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, or professional, this article aims to provide a detailed and multi-dimensional introduction to these essential components.
What is a Differential Input Op Amp?
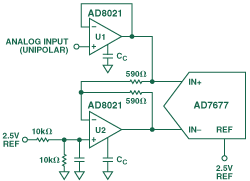
A differential input op amp is a type of operational amplifier that has two input terminals: a non-inverting input (+) and an inverting input (-). The primary difference between a differential input op amp and a single-ended input op amp is that it can process signals with a common-mode voltage, which is the voltage level shared by both input terminals.
One of the key advantages of a differential input op amp is its ability to reject common-mode noise. This noise can come from various sources, such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or power supply fluctuations. By comparing the voltage levels at both input terminals, the op amp can effectively cancel out the common-mode noise, leaving only the differential signal (the difference between the two input voltages) to be amplified.
How Does a Differential Input Op Amp Work?
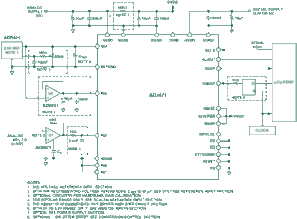
A differential input op amp operates based on the principle of negative feedback. When a differential signal is applied to the input terminals, the op amp compares the voltage levels at both terminals. If the voltage at the inverting input is higher than the non-inverting input, the op amp will amplify the difference between the two voltages and output a negative voltage. Conversely, if the voltage at the inverting input is lower than the non-inverting input, the op amp will amplify the difference and output a positive voltage.
The amplification factor of a differential input op amp is determined by the external components connected to the op amp, such as resistors and capacitors. These components can be used to adjust the gain, bandwidth, and other characteristics of the op amp.
Applications of Differential Input Op Amps
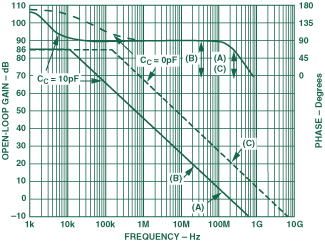
Differential input op amps are widely used in various applications due to their ability to reject common-mode noise and provide high input impedance. Some common applications include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Signal Conditioning | Used to amplify, filter, and shape signals for further processing. |
| Instrumentation Amplifiers | Used to amplify small differential signals with high common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR). |
| Communication Systems | Used to process and amplify signals in wireless and wired communication systems. |
| Medical Equipment | Used to amplify and process physiological signals in medical devices. |
These are just a few examples of the many applications where differential input op amps play a crucial role. Their versatility and performance make them an indispensable component in the field of analog electronics.
Choosing the Right Differential Input Op Amp
When selecting a differential input op amp for your project, there are several factors to consider:
- Gain and Bandwidth: Ensure that the op amp has the desired gain and bandwidth for your application.
- CMRR: Choose an op amp with a high CMRR to minimize common-mode noise.
- Input and Output Impedance: Select an op amp with appropriate input and output impedance for your circuit.
- Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR): A high PSRR is desirable to minimize the impact of power supply fluctuations on the op amp’s performance.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right differential input op amp for your specific application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, differential input op amps are essential components in the field of analog electronics. Their ability to reject common-mode noise and provide high input impedance makes them ideal for a wide range of applications. By understanding the basics of how these op amps work and the factors to consider when selecting one, you can effectively incorporate them into your projects and achieve optimal performance.
