Understanding the Unity Gain Op Amp Circuit: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electronic circuits, the unity gain op amp circuit is a fundamental and highly versatile design. It’s a staple in many applications, from audio amplification to signal conditioning. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the unity gain op amp circuit, exploring its design, operation, and practical applications.
What is a Unity Gain Op Amp Circuit?
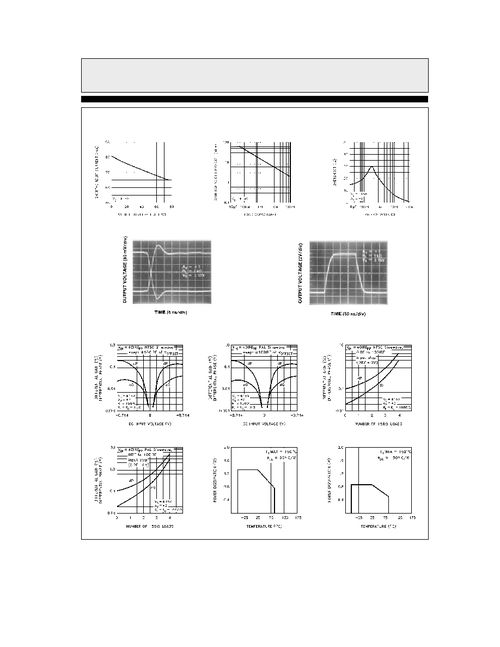
A unity gain op amp circuit is a configuration where the op amp is used with a feedback resistor network that provides a gain of exactly one (or unity). This means that the output voltage is the same as the input voltage, hence the name “unity gain.” Despite its simplicity, this circuit is incredibly useful due to its ability to buffer signals, isolate circuits, and provide a stable reference voltage.
Components of a Unity Gain Op Amp Circuit
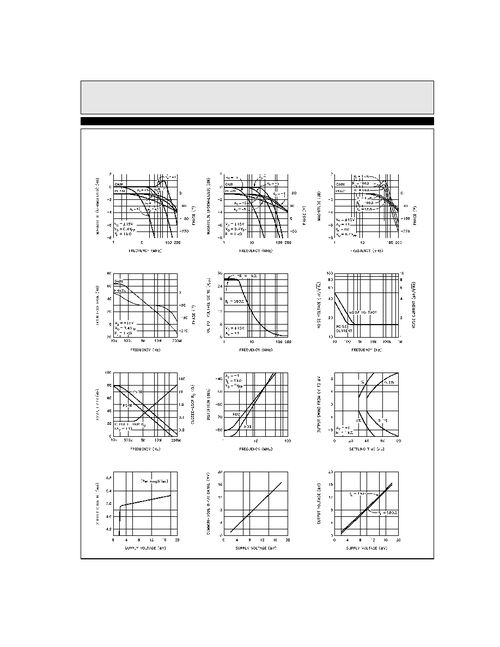
The basic components of a unity gain op amp circuit include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) | The core of the circuit, an op amp is a high-gain voltage amplifier with differential inputs and a single output. |
| Feedback Resistor Network | This network consists of resistors that provide the necessary feedback to achieve unity gain. |
| Input Signal | The signal to be amplified or buffered. |
| Output Signal | The amplified or buffered signal. |
How Does a Unity Gain Op Amp Circuit Work?
In a unity gain op amp circuit, the op amp operates in an open-loop configuration, meaning that there is no feedback path from the output to the inverting input. This results in a very high gain, which can be problematic if not properly controlled. To achieve unity gain, a feedback resistor network is connected between the output and the inverting input.
When the input signal is applied to the non-inverting input, the op amp tries to maintain the voltage difference between its inputs at zero. Since the inverting input is grounded, the op amp drives its output to a voltage level that will cause the voltage at the inverting input to be equal to the voltage at the non-inverting input. This voltage level is the same as the input signal, resulting in a gain of one.
Advantages of a Unity Gain Op Amp Circuit
There are several advantages to using a unity gain op amp circuit:
-
Signal Buffering: The circuit can be used to buffer signals, which helps to prevent signal degradation and improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
-
Isolation: The circuit can isolate different parts of a circuit, preventing interference and ensuring that the output signal is not affected by the input signal or other circuit components.
-
Stable Reference Voltage: The circuit can be used to generate a stable reference voltage, which is essential for many applications.
-
Low Output Impedance: The output impedance of the circuit is low, which means that it can drive loads with minimal signal loss.
Practical Applications of a Unity Gain Op Amp Circuit
The unity gain op amp circuit has a wide range of practical applications, including:
-
Audio Amplification: The circuit can be used to amplify audio signals, such as those from a microphone or line input.
-
Signal Conditioning: The circuit can be used to condition signals, such as filtering, amplifying, and buffering.
-
Instrumentation: The circuit can be used in instrumentation applications, such as measuring and controlling electrical signals.
-
Power Supply Regulation: The circuit can be used to regulate power supply voltages, ensuring that the output voltage is stable and accurate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the unity gain op amp circuit is a fundamental and versatile design that has many practical applications. By understanding its design, operation, and advantages, you can effectively utilize this circuit in your electronic projects. Whether you’re working on audio amplification, signal conditioning, or any other electronic application,
