An operational amplifier isolation circuit is designed to prevent unwanted interaction between different parts of a system by electrically separating them. This is typically achieved using an isolation amplifier, which consists of an input amplifier, an isolation barrier, and an output amplifier. The isolation barrier can be implemented using various technologies, such as transformers, capacitors, or optocouplers.
Here are some key aspects of an op amp isolation circuit:
1. Functionality: The primary purpose of an isolation circuit is to maintain the integrity of the signal while preventing direct electrical connection between the input and output stages. This is crucial in applications where there is a risk of ground loops, noise coupling, or high voltage differences that could damage the circuit or affect its performance.
2. Signal Transfer: The input amplifier receives the signal and amplifies it before it is passed through the isolation barrier. The output amplifier then amplifies the signal again to compensate for any loss that may have occurred during the isolation process.
3. Isolation Barrier: The isolation barrier is the heart of the circuit and is responsible for the electrical separation. Transformers are commonly used for lowfrequency applications, while capacitors and optocouplers are suitable for highfrequency signals. The choice of isolation technology depends on factors such as the frequency range, voltage levels, and power requirements.
4. Grounding: In an isolation circuit, the input and output stages are typically referenced to different ground points. This helps to prevent ground loops and minimize noise coupling.
5. Applications: Op amp isolation circuits are widely used in various applications, including industrial control systems, medical equipment, and automotive electronics. They are particularly useful in environments where there is a risk of electrical noise, ground loops, or high voltage differences.
6. Design Considerations: When designing an op amp isolation circuit, it is important to consider factors such as the input and output voltage ranges, the required bandwidth, the isolation voltage, and the power supply requirements. The choice of components, such as the op amp, isolation amplifier, and isolation technology, should be based on these specifications.
In summary, an op amp isolation circuit is a crucial component in many electronic systems, providing electrical separation between different parts of the system while maintaining signal integrity. The design and implementation of such circuits require careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability.你有没有想过,那些看似普通的电子设备里,其实隐藏着不少高科技的奥秘呢?比如,今天咱们就要聊聊一个听起来有点儿高大上的东西——运算放大器隔离电路(简称op amp isolation circuit)。这可不是什么高不可攀的科技,它就在我们身边,默默地为我们的生活提供便利。接下来,就让我带你一探究竟吧!
什么是运算放大器隔离电路?
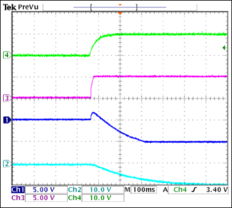
首先,得先弄明白什么是运算放大器。运算放大器,简称op amp,是一种常见的电子元件,它具有高增益、高输入阻抗、低输出阻抗等特点。而隔离电路,顾名思义,就是用来隔离电路的,防止信号干扰和电源噪声。
将这两个东西结合起来,就形成了运算放大器隔离电路。简单来说,它就像一个“保护罩”,将信号和电源隔离开来,确保信号传输的稳定性和安全性。
运算放大器隔离电路的应用

运算放大器隔离电路的应用范围非常广泛,几乎涵盖了电子设备的方方面面。以下是一些常见的应用场景:
1. 工业控制领域:在工业控制系统中,运算放大器隔离电路可以用于隔离传感器信号和控制系统,防止干扰和噪声对系统的影响。
2. 医疗设备:在医疗设备中,运算放大器隔离电路可以用于隔离患者信号和医疗设备,确保患者安全。
3. 通信设备:在通信设备中,运算放大器隔离电路可以用于隔离信号传输线路,提高通信质量。
4. 家用电器:在家用电器中,运算放大器隔离电路可以用于隔离电源和信号传输线路,防止电磁干扰。
运算放大器隔离电路的工作原理
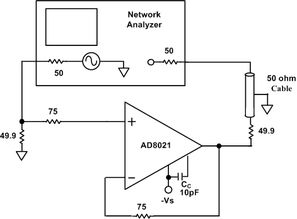
运算放大器隔离电路的工作原理其实很简单。它主要由以下几个部分组成:
1. 运算放大器:负责放大信号,提高信号增益。
2. 隔离变压器:将信号和电源隔离开来,防止干扰和噪声。
3. 反馈电路:用于调整信号增益,确保信号传输的稳定性。
4. 滤波电路:用于滤除信号中的噪声和干扰。
当信号通过运算放大器放大后,再经过隔离变压器和滤波电路,最终输出一个稳定、干净的信号。
运算放大器隔离电路的优势
运算放大器隔离电路具有以下优势:
1. 高隔离度:可以有效隔离信号和电源,防止干扰和噪声。
2. 高稳定性:信号传输稳定,不受外界环境的影响。
3. 高可靠性:电路结构简单,故障率低。
4. 广泛应用:适用于各种电子设备,具有很高的实用价值。
运算放大器隔离电路虽然听起来有些复杂,但其实在我们的生活中无处不在。它为我们的生活提供了便利,提高了电子设备的性能。所以,下次当你看到一款电子设备时,不妨想想,这其中可能就蕴含着运算放大器隔离电路的智慧。这可是电子科技的魅力所在哦!
