Op Amp Feedback Circuits: A Comprehensive Guide
Operational amplifiers (op-amps) are versatile electronic components widely used in various feedback circuits. These circuits play a crucial role in amplifying, filtering, and stabilizing signals. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of op-amp feedback circuits, exploring their types, applications, and design considerations.
Understanding Op-Amp Feedback Circuits

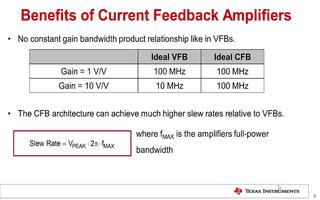
Op-amp feedback circuits are designed to utilize the feedback mechanism of an op-amp to control its gain and stability. Feedback can be classified into two types: voltage feedback and current feedback. Voltage feedback is the most common type, where the output voltage is compared with the input voltage, and the difference is used to adjust the gain. Current feedback, on the other hand, compares the output current with the input current.
Op-amps are available in various configurations, such as inverting, non-inverting, and differential amplifiers. Each configuration has its unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will focus on the inverting and non-inverting amplifiers, as they are the most widely used in feedback circuits.
Inverting Amplifier
The inverting amplifier is a fundamental op-amp configuration that provides a negative gain. It is characterized by its high input impedance and low output impedance. The gain of an inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (Rf) to the input resistor (Rin). The formula for gain is given by:
| Gain | Formula |
|---|---|
| A | A = -Rf/Rin |
One of the key advantages of the inverting amplifier is its high input impedance, which allows it to drive high-impedance loads without affecting the source. This makes it suitable for applications such as signal conditioning, filtering, and voltage followers.
Non-Inverting Amplifier
The non-inverting amplifier is another popular op-amp configuration that provides a positive gain. It has a high input impedance and a low output impedance, similar to the inverting amplifier. The gain of a non-inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (Rf) to the input resistor (Rin), but with a positive sign. The formula for gain is given by:
| Gain | Formula |
|---|---|
| A | A = 1 + Rf/Rin |
The non-inverting amplifier is ideal for applications that require a high input impedance, such as voltage followers, summing amplifiers, and active filters. It also provides a stable gain, as the feedback is applied to the non-inverting input, which reduces the effect of temperature variations and component tolerances.
Applications of Op-Amp Feedback Circuits
Op-amp feedback circuits find applications in various fields, including audio amplification, signal processing, and data acquisition. Some common applications include:
-
Audio amplifiers: Op-amp feedback circuits are widely used in audio amplifiers to provide high-fidelity sound reproduction.
-
Signal conditioning: Feedback circuits can be used to filter, amplify, and shape signals for further processing.
-
Data acquisition: Op-amps are used in data acquisition systems to convert analog signals into digital values for processing and analysis.
-
Control systems: Feedback circuits are essential in control systems for maintaining stability and accuracy.
Design Considerations
Designing op-amp feedback circuits requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance. Some key design considerations include:
-
Component selection: Choosing the right op-amp and resistors is crucial for achieving the desired gain, bandwidth, and stability.
-
Power supply: The power supply voltage should be adequate to provide the required output voltage and current.
-
Temperature compensation: Op-amps may exhibit temperature variations, which can affect the circuit’s performance. Temperature compensation techniques can be employed to mitigate this issue.
-
Stability analysis: It is essential
