Understanding the PSRR OP Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to operational amplifiers (op-amps), the PSRR (Power Supply Rejection Ratio) is a crucial parameter that determines the amplifier’s ability to reject noise on its power supply lines. In this detailed guide, we will delve into the intricacies of PSRR in op-amps, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and practical applications.
What is PSRR?
PSRR stands for Power Supply Rejection Ratio, which is a measure of an op-amp’s ability to reject noise on its power supply lines. It is defined as the ratio of the voltage change at the output to the voltage change at the power supply input. A higher PSRR value indicates better noise rejection capabilities.
PSRR is typically expressed in decibels (dB) and can be categorized into two types: AC PSRR and DC PSRR. AC PSRR measures the rejection of AC noise, while DC PSRR measures the rejection of DC noise. Both parameters are important in different applications.
Significance of PSRR in Op-Amps
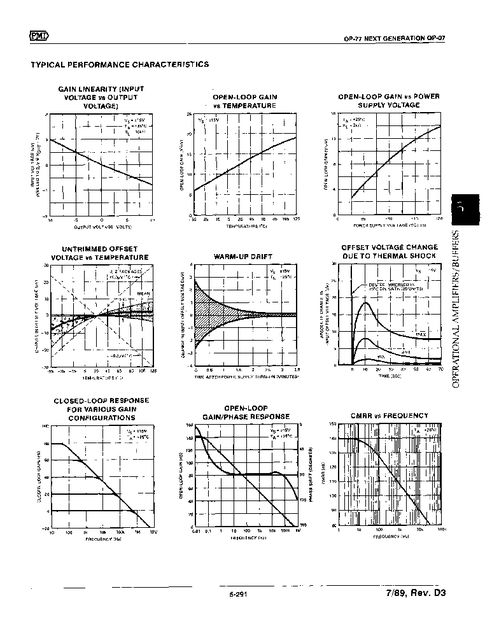
PSRR is a critical parameter in op-amps for several reasons:
-
Improved Signal Quality: By rejecting noise on the power supply lines, PSRR ensures that the output signal is clean and free from unwanted disturbances.
-
Enhanced Performance: A higher PSRR value allows the op-amp to operate more effectively in noisy environments, resulting in better overall performance.
-
Increased Stability: PSRR helps in maintaining stability in the amplifier’s operation, especially in high-impedance circuits.
Factors Affecting PSRR
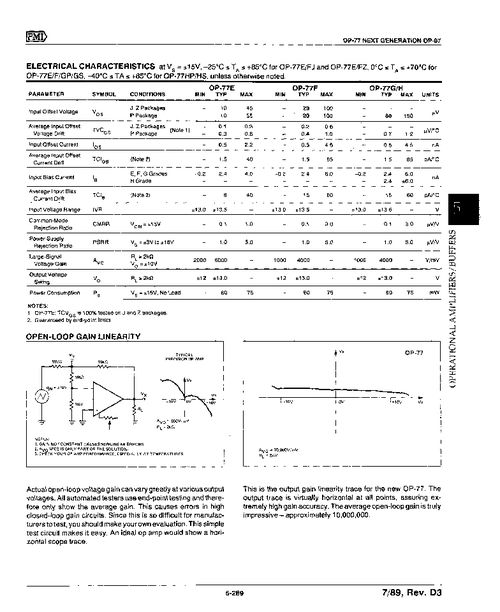
Several factors can influence the PSRR of an op-amp:
-
Op-Amp Architecture: The internal design of the op-amp plays a significant role in determining its PSRR. Different architectures, such as bipolar, MOSFET, and JFET, have varying PSRR characteristics.
-
Power Supply Rejection Capacitors: These capacitors are used to filter out noise on the power supply lines and can significantly impact the PSRR of an op-amp.
-
Temperature: PSRR can vary with temperature, and this variation should be considered when designing circuits.
-
Supply Voltage: The PSRR of an op-amp can change with the supply voltage, and this should be taken into account when selecting an op-amp for a specific application.
Practical Applications of PSRR in Op-Amps
PSRR is essential in various applications, including:
-
Audio Equipment: PSRR helps in reducing noise and improving the quality of audio signals in devices like speakers, headphones, and amplifiers.
-
Medical Equipment: In medical devices, PSRR ensures accurate and reliable measurements by minimizing noise interference.
-
Instrumentation: PSRR is crucial in data acquisition systems and sensors, where noise rejection is essential for accurate readings.
-
Power Supplies: PSRR helps in designing power supplies with better noise rejection capabilities, resulting in cleaner output.
Table: PSRR Comparison of Different Op-Amp Architectures
| Op-Amp Architecture | AC PSRR (dB) | DC PSRR (dB) |
|---|---|---|
| Bipolar | 80-100 | 60-80 |
| MOSFET | 100-120 | 80-100 |
| JFET | 90-110 | 70-90 |
As shown in the table, MOSFET-based op-amps generally offer the best PSRR performance, followed by bipolar and JFET-based op-amps.
Conclusion
PSRR is a vital parameter in op-amps, determining their ability to reject noise on the power supply lines
