Op Amp Examples: A Comprehensive Guide
Operational amplifiers, or op amps, are versatile electronic devices that have found their way into countless applications across various fields. Whether you’re a hobbyist, an engineer, or simply curious about electronics, understanding how op amps work and their various applications can be incredibly beneficial. In this article, we’ll delve into some of the most common op amp examples, exploring their functionalities and the roles they play in different circuits.
Basic Op-Amp Configuration: Inverting Amplifier
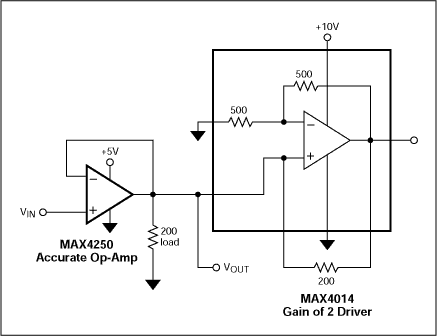
The inverting amplifier is one of the most fundamental op amp configurations. As the name suggests, it inverts the input signal while amplifying it. This configuration is achieved by connecting the input signal to the inverting input terminal (-) of the op amp and grounding the non-inverting input terminal (+). The output is taken from the output terminal of the op amp.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Op Amp | Operational Amplifier |
| Input Signal | Signal to be amplified |
| Feedback Resistor (Rf) | Connected between output and inverting input |
| Input Resistor (Ri) | Connected between input signal and inverting input |
The gain of the inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (Rf) to the input resistor (Ri). For example, if Rf is 10k惟 and Ri is 1k惟, the gain will be 10. This configuration is widely used in audio amplifiers, signal conditioning, and filtering applications.
Non-Inverting Amplifier
The non-inverting amplifier is another popular op amp configuration. Unlike the inverting amplifier, it does not invert the input signal. Instead, it amplifies the input signal while maintaining its phase. The non-inverting amplifier is achieved by connecting the input signal to the non-inverting input terminal (+) of the op amp and grounding the inverting input terminal (-). The output is taken from the output terminal of the op amp.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Op Amp | Operational Amplifier |
| Input Signal | Signal to be amplified |
| Feedback Resistor (Rf) | Connected between output and non-inverting input |
| Input Resistor (Ri) | Connected between input signal and non-inverting input |
The gain of the non-inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (Rf) to the input resistor (Ri). For example, if Rf is 10k惟 and Ri is 1k惟, the gain will be 10. This configuration is commonly used in audio amplifiers, signal conditioning, and voltage follower applications.
Op-Amp as a Comparator
An op amp can also be used as a comparator. In this configuration, the op amp compares the voltages at its inverting and non-inverting input terminals. If the voltage at the non-inverting input is higher than the voltage at the inverting input, the output will be high; otherwise, it will be low. This configuration is useful in various applications, such as threshold detection, voltage monitoring, and signal switching.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Op Amp | Operational Amplifier |
| Input Signal 1 | Signal to be compared |
| Input Signal 2 | Reference voltage |
