Buffer Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Buffer operational amplifiers, often referred to as buffer op amps, are essential components in electronic circuits. They are designed to provide a high input impedance and a low output impedance, which makes them ideal for interfacing between different circuit elements. In this article, we will delve into the details of buffer op amps, their applications, and how they work.
Understanding Buffer Op Amps
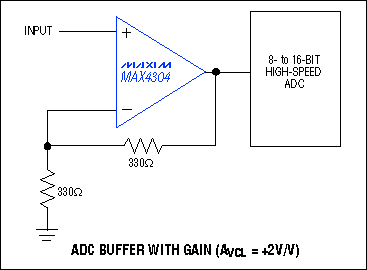
Buffer op amps are a type of operational amplifier that is specifically designed to act as a buffer. Unlike standard op amps, which have a high gain, buffer op amps have a gain of one. This means that the output voltage of a buffer op amp is equal to the input voltage, with minimal distortion and noise.
One of the key features of buffer op amps is their high input impedance. This allows them to draw very little current from the input signal source, which is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the signal. Additionally, buffer op amps have a low output impedance, which means they can drive loads with minimal voltage drop.
Buffer op amps are typically available in various configurations, including single, dual, and quad packages. The choice of package depends on the specific requirements of the circuit.
Applications of Buffer Op Amps
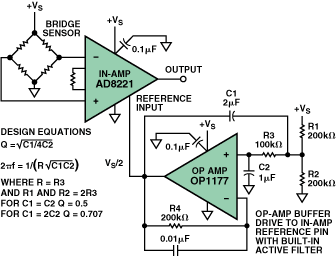
Buffer op amps find applications in a wide range of electronic circuits. Some of the most common uses include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Signal Conditioning | Buffer op amps are used to condition signals, such as amplifying, filtering, and shaping them, to meet the requirements of subsequent circuit stages. |
| Impedance Matching | They are used to match the input impedance of a circuit to the output impedance of a signal source, ensuring optimal signal transfer. |
| Isolation | Buffer op amps can isolate sensitive circuit sections from noise and other骞叉壈 sources. |
| Level Shifting | They are used to shift the voltage level of a signal to match the voltage levels of different circuit sections. |
Buffer op amps are also used in audio circuits, data acquisition systems, and many other applications where signal integrity is critical.
How Buffer Op Amps Work

Buffer op amps work on the principle of negative feedback. In a negative feedback configuration, a portion of the output voltage is fed back to the inverting input of the op amp. This feedback signal is then compared to the input signal, and the op amp adjusts its output to minimize the difference between the two.
Because the gain of a buffer op amp is one, the feedback signal is equal to the input signal. This ensures that the output voltage is an exact replica of the input voltage, with minimal distortion and noise.
Buffer op amps are typically powered by a dual supply voltage, which allows them to operate over a wide range of voltages. They can also be powered by a single supply voltage, although this may limit their operating range.
Choosing the Right Buffer Op Amp
When selecting a buffer op amp for a specific application, several factors need to be considered:
-
Supply Voltage: Ensure that the buffer op amp can operate within the supply voltage range of your circuit.
-
Input and Output Impedance: Choose an op amp with the appropriate input and output impedance for your application.
-
Bandwidth: Select an op amp with a sufficient bandwidth to handle the frequency range of your signal.
-
Power Consumption: Consider the power consumption of the op amp, especially in battery-powered applications.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right buffer op amp for your specific application.
Conclusion
Buffer op amps are essential components in electronic circuits, providing a high input impedance and a low output impedance. They find applications in a wide range of circuits, from signal conditioning to impedance matching. By understanding how buffer op amps work and how to choose the right one for your application, you can ensure the optimal performance of your electronic circuits.
