Inverting Amplifier Op Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the inverting amplifier operational amplifier (op amp) is crucial for anyone delving into the world of analog electronics. This guide will walk you through the intricacies of an inverting amplifier, its working principle, applications, and key specifications. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of this essential component.
What is an Inverting Amplifier Op Amp?
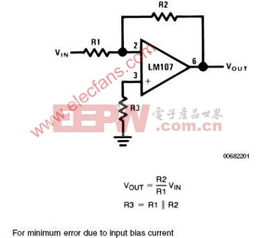
An inverting amplifier is a type of operational amplifier circuit that provides an inverted output signal relative to the input signal. It is widely used in various applications, such as signal conditioning, filtering, and amplification. The key feature of an inverting amplifier is its negative feedback, which ensures stability and linearity.
Working Principle of an Inverting Amplifier Op Amp
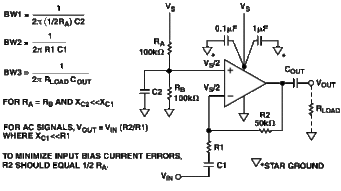
The working principle of an inverting amplifier op amp is based on the concept of negative feedback. The input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal (-) of the op amp, while the output signal is taken from the output terminal. The non-inverting input terminal (+) is connected to a voltage reference, typically ground.
When the input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal, it creates a voltage difference between the two input terminals. This voltage difference is amplified by the open-loop gain of the op amp. The amplified signal is then fed back to the inverting input terminal through a feedback resistor (Rf). The feedback resistor determines the gain of the inverting amplifier.
Key Components of an Inverting Amplifier Op Amp
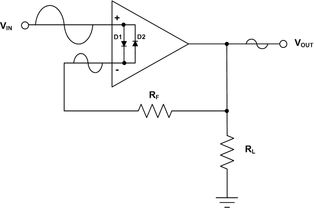
The key components of an inverting amplifier op amp include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Op Amp | The operational amplifier is the core component of the inverting amplifier. It provides the amplification and stability required for the circuit. |
| Input Signal | The input signal is applied to the inverting input terminal of the op amp. |
| Feedback Resistor (Rf) | The feedback resistor determines the gain of the inverting amplifier. The gain is calculated as -Rf/Rin, where Rin is the input resistor. |
| Input Resistor (Rin) | The input resistor provides a path for the input signal to reach the inverting input terminal of the op amp. |
Applications of Inverting Amplifier Op Amp
Inverting amplifiers find applications in various fields, including:
- Signal Conditioning: Inverting amplifiers can be used to amplify and filter signals, making them suitable for applications such as sensor interfacing and data acquisition.
- Amplification: They can be used to amplify low-level signals, such as those from sensors or transducers.
- Filtering: Inverting amplifiers can be used to implement low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters.
- Summing Amplifiers: They can be used to sum multiple input signals.
Key Specifications of Inverting Amplifier Op Amp
When selecting an inverting amplifier op amp, it is essential to consider the following key specifications:
- Open-loop Gain: The open-loop gain of an op amp determines the maximum gain that can be achieved with negative feedback. A higher open-loop gain allows for greater flexibility in designing the circuit.
- Input Offset Voltage: The input offset voltage is the voltage difference between the two input terminals when the input signal is zero. A lower input offset voltage is desirable for better accuracy.
- Input Bias Current: The input bias current is the current flowing into the input terminals of the op amp. A lower input bias current is preferable for minimizing errors in the circuit.
- Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR): The PSRR measures the ability of the op amp to reject noise and fluctuations in the power supply voltage. A higher PSRR is desirable for better performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the inverting amplifier op amp is essential for anyone working in the field of analog electronics. By grasping the working principle, key components, applications, and specifications, you can design and implement effective circuits for various applications. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional
