Non-Inverting Amplifier Op-Amp: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electronic amplification, the non-inverting amplifier op-amp is a cornerstone of analog circuit design. This versatile component allows for precise amplification of signals without phase inversion, making it a favorite among engineers and hobbyists alike. In this detailed guide, we will explore the intricacies of the non-inverting amplifier op-amp, its applications, and how to design it effectively.
Understanding the Non-Inverting Amplifier Op-Amp
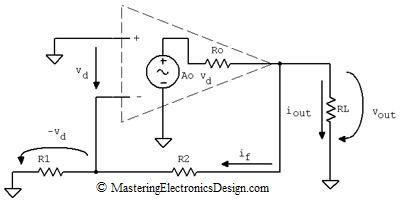
The non-inverting amplifier op-amp is a type of operational amplifier that provides voltage gain without phase inversion. It is called “non-inverting” because the input signal is applied to the non-inverting input terminal of the op-amp. This configuration ensures that the output signal is in phase with the input signal, which is often desirable in many applications.
Here’s a basic diagram of a non-inverting amplifier op-amp:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Op-Amp | Operational Amplifier |
| Input Signal | Signal to be amplified |
| Feedback Resistor (Rf) | Resistor connected between the output and the inverting input |
| Input Resistor (Ri) | Resistor connected between the input signal and the inverting input |
The gain of the non-inverting amplifier is determined by the ratio of the feedback resistor (Rf) to the input resistor (Ri). The formula for gain is:
Gain = 1 + (Rf / Ri)
This formula shows that the gain is directly proportional to the ratio of Rf to Ri, and it can be adjusted by changing the values of these resistors.
Applications of Non-Inverting Amplifier Op-Amp
The non-inverting amplifier op-amp has a wide range of applications due to its linear and stable gain characteristics. Some common applications include:
-
Signal conditioning
-
Signal amplification
-
Filter design
-
Instrumentation amplifiers
-
Audio amplifiers
Designing a Non-Inverting Amplifier Op-Amp
Designing a non-inverting amplifier op-amp involves selecting the appropriate op-amp, determining the desired gain, and choosing the right resistor values. Here are some key considerations:
-
Select an op-amp with a wide bandwidth and low noise to ensure accurate amplification.
-
Choose the desired gain based on the application requirements.
-
Calculate the resistor values using the gain formula (Gain = 1 + (Rf / Ri)).
-
Ensure that the power supply voltage is sufficient to provide the required output voltage swing.
Practical Tips for Designing Non-Inverting Amplifier Op-Amp Circuits
When designing a non-inverting amplifier op-amp circuit, keep the following tips in mind:
-
Use a breadboard or PCB for prototyping to easily modify the circuit.
-
Choose resistors with high precision to minimize gain errors.
-
Consider the input and output impedance of the op-amp when selecting components.
-
Use a power supply with a stable voltage to ensure consistent performance.
Conclusion
The non-inverting amplifier op-amp is a powerful and versatile tool for electronic amplification. By understanding its principles, applications, and design considerations, you can create effective and precise amplification circuits for a wide range of applications. Whether you’re an engineer or a hobbyist, the non-inverting amplifier op-amp is a valuable component to have in your toolkit.
